Stability Analysis of Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Stiff Linear Differential Equations
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2024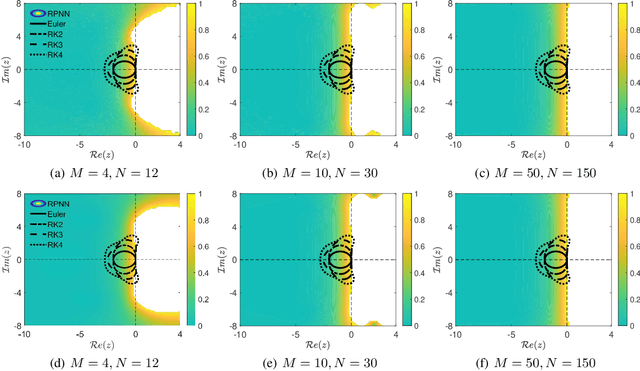
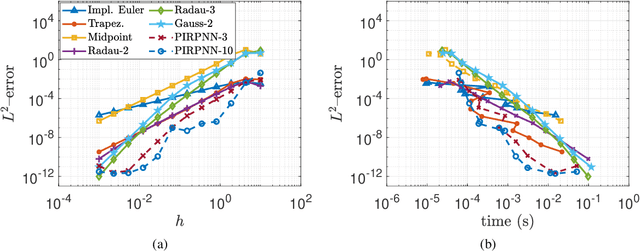
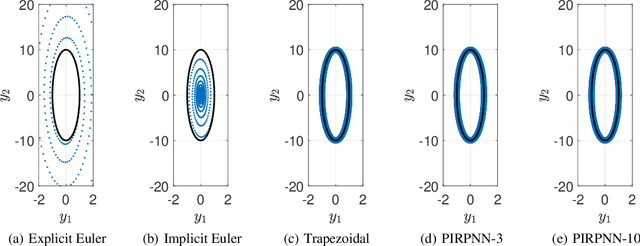
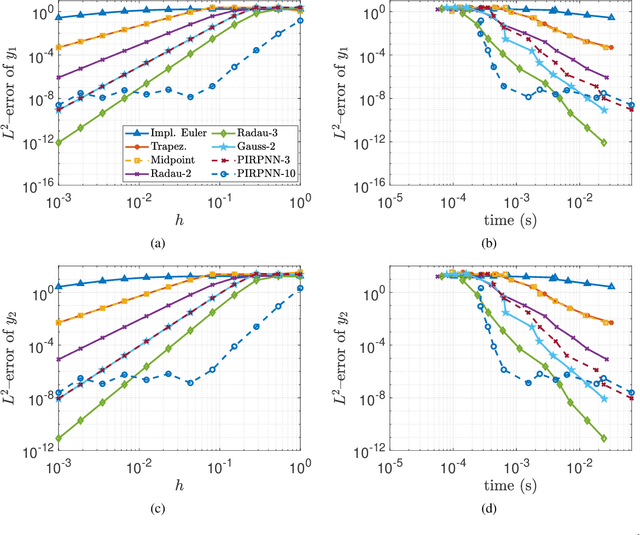
We present a stability analysis of Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) coupled with random projections, for the numerical solution of (stiff) linear differential equations. For our analysis, we consider systems of linear ODEs, and linear parabolic PDEs. We prove that properly designed PINNs offer consistent and asymptotically stable numerical schemes, thus convergent schemes. In particular, we prove that multi-collocation random projection PINNs guarantee asymptotic stability for very high stiffness and that single-collocation PINNs are $A$-stable. To assess the performance of the PINNs in terms of both numerical approximation accuracy and computational cost, we compare it with other implicit schemes and in particular backward Euler, the midpoint, trapezoidal (Crank-Nikolson), the 2-stage Gauss scheme and the 2 and 3 stages Radau schemes. We show that the proposed PINNs outperform the above traditional schemes, in both numerical approximation accuracy and importantly computational cost, for a wide range of step sizes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge