SqueezeSegV2: Improved Model Structure and Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Road-Object Segmentation from a LiDAR Point Cloud
Paper and Code
Sep 22, 2018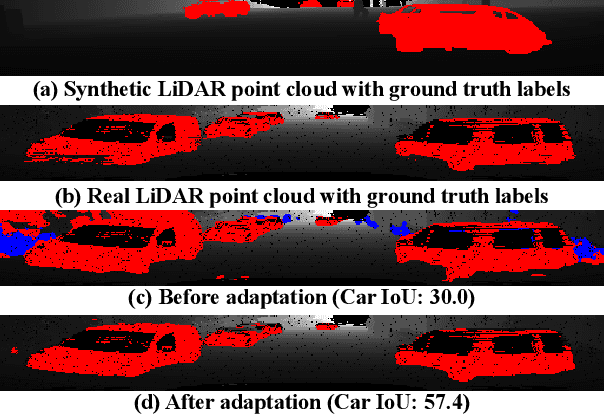
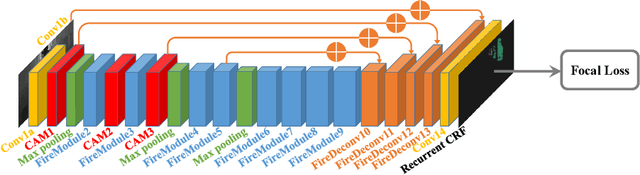
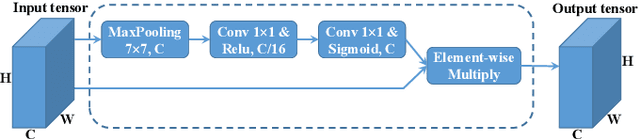
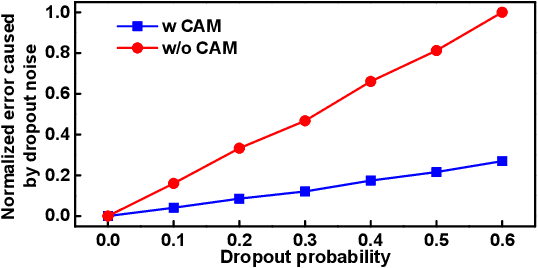
Earlier work demonstrates the promise of deep-learning-based approaches for point cloud segmentation; however, these approaches need to be improved to be practically useful. To this end, we introduce a new model SqueezeSegV2 that is more robust to dropout noise in LiDAR point clouds. With improved model structure, training loss, batch normalization and additional input channel, SqueezeSegV2 achieves significant accuracy improvement when trained on real data. Training models for point cloud segmentation requires large amounts of labeled point-cloud data, which is expensive to obtain. To sidestep the cost of collection and annotation, simulators such as GTA-V can be used to create unlimited amounts of labeled, synthetic data. However, due to domain shift, models trained on synthetic data often do not generalize well to the real world. We address this problem with a domain-adaptation training pipeline consisting of three major components: 1) learned intensity rendering, 2) geodesic correlation alignment, and 3) progressive domain calibration. When trained on real data, our new model exhibits segmentation accuracy improvements of 6.0-8.6% over the original SqueezeSeg. When training our new model on synthetic data using the proposed domain adaptation pipeline, we nearly double test accuracy on real-world data, from 29.0% to 57.4%. Our source code and synthetic dataset will be open-sourced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge