Spherical formulation of moving object geometric constraints for monocular fisheye cameras
Paper and Code
Mar 06, 2020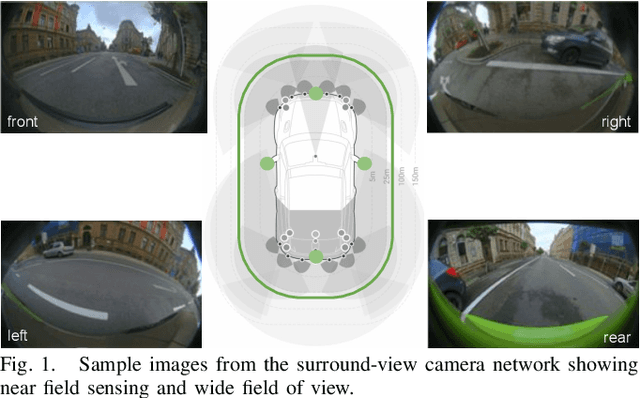
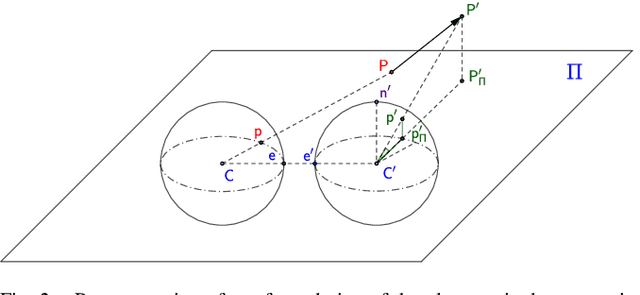
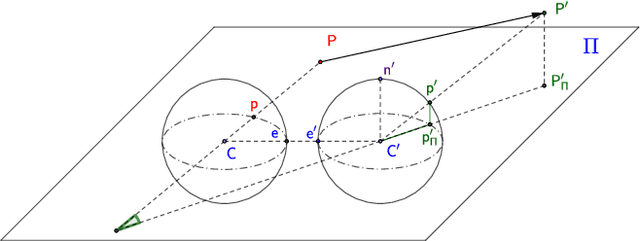
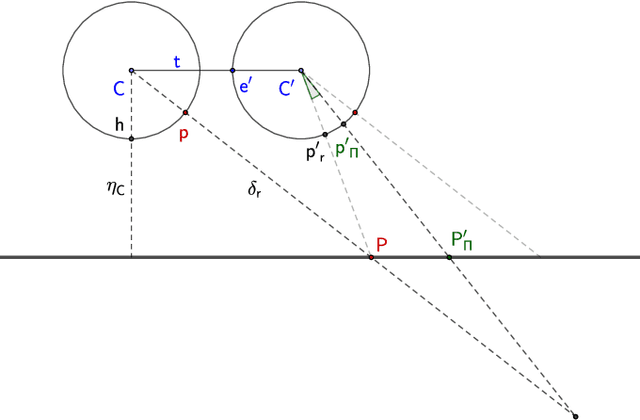
In this paper, we introduce a moving object detection algorithm for fisheye cameras used in autonomous driving. We reformulate the three commonly used constraints in rectilinear images (epipolar, positive depth and positive height constraints) to spherical coordinates which is invariant to specific camera configuration once the calibration is known. One of the main challenging use case in autonomous driving is to detect parallel moving objects which suffer from motion-parallax ambiguity. To alleviate this, we formulate an additional fourth constraint, called the anti-parallel constraint, which aids the detection of objects with motion that mirrors the ego-vehicle possible. We analyze the proposed algorithm in different scenarios and demonstrate that it works effectively operating directly on fisheye images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge