Speech Enhancement Based on Cyclegan with Noise-informed Training
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2021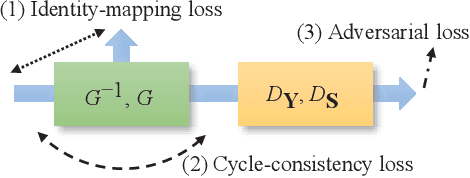
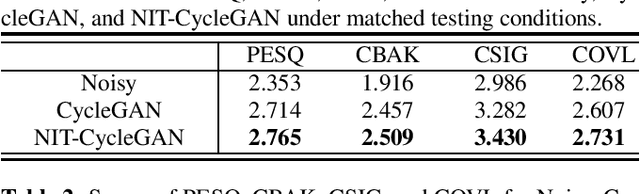
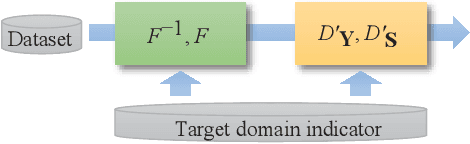
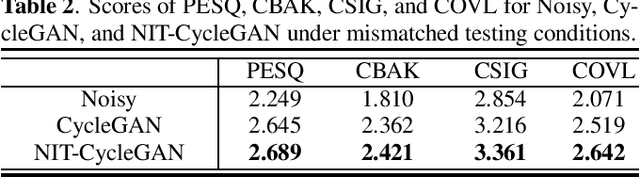
Speech enhancement (SE) approaches can be classified into supervised and unsupervised categories. For unsupervised SE, a well-known cycle-consistent generative adversarial network (CycleGAN) model, which comprises two generators and two discriminators, has been shown to provide a powerful nonlinear mapping ability and thus achieve a promising noise-suppression capability. However, a low-efficiency training process along with insufficient knowledge between noisy and clean speech may limit the enhancement performance of the CycleGAN SE at runtime. In this study, we propose a novel noise-informed-training CycleGAN approach that incorporates additional inputs into the generators and discriminators to assist the CycleGAN in learning a more accurate transformation of speech signals between the noise and clean domains. The additional input feature serves as an indicator that provides more information during the CycleGAN training stage. Experiment results confirm that the proposed approach can improve the CycleGAN SE model while achieving a better sound quality and fewer signal distortions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge