Speaker anonymization using neural audio codec language models
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2023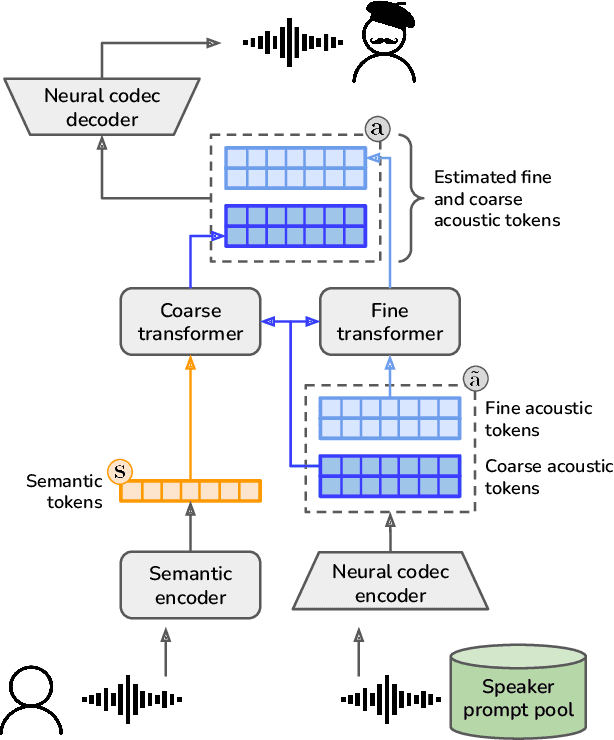
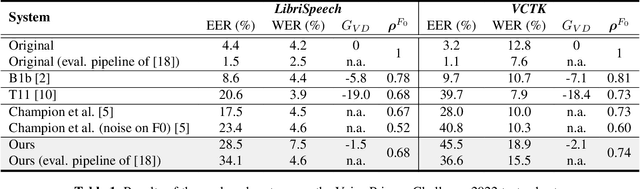
The vast majority of approaches to speaker anonymization involve the extraction of fundamental frequency estimates, linguistic features and a speaker embedding which is perturbed to obfuscate the speaker identity before an anonymized speech waveform is resynthesized using a vocoder. Recent work has shown that x-vector transformations are difficult to control consistently: other sources of speaker information contained within fundamental frequency and linguistic features are re-entangled upon vocoding, meaning that anonymized speech signals still contain speaker information. We propose an approach based upon neural audio codecs (NACs), which are known to generate high-quality synthetic speech when combined with language models. NACs use quantized codes, which are known to effectively bottleneck speaker-related information: we demonstrate the potential of speaker anonymization systems based on NAC language modeling by applying the evaluation framework of the Voice Privacy Challenge 2022.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge