Sparsity May Cry: Let Us Fail Sparse Neural Networks Together!
Paper and Code
Mar 03, 2023

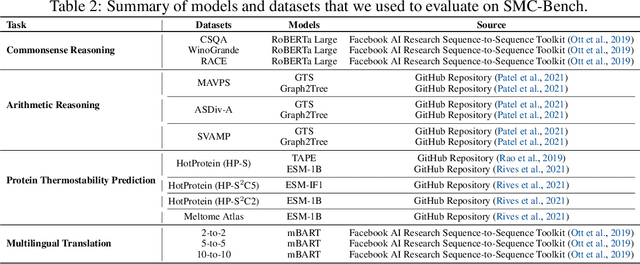

Sparse Neural Networks (SNNs) have received voluminous attention predominantly due to growing computational and memory footprints of consistently exploding parameter count in large-scale models. Similar to their dense counterparts, recent SNNs generalize just as well and are equipped with numerous favorable benefits (e.g., low complexity, high scalability, and robustness), sometimes even better than the original dense networks. As research effort is focused on developing increasingly sophisticated sparse algorithms, it is startling that a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the effectiveness of these algorithms has been highly overlooked. In absence of a carefully crafted evaluation benchmark, most if not all, sparse algorithms are evaluated against fairly simple and naive tasks (eg. CIFAR, ImageNet, GLUE, etc.), which can potentially camouflage many advantages as well unexpected predicaments of SNNs. In pursuit of a more general evaluation and unveiling the true potential of sparse algorithms, we introduce "Sparsity May Cry" Benchmark (SMC-Bench), a collection of carefully-curated 4 diverse tasks with 10 datasets, that accounts for capturing a wide range of domain-specific and sophisticated knowledge. Our systemic evaluation of the most representative sparse algorithms reveals an important obscured observation: the state-of-the-art magnitude- and/or gradient-based sparse algorithms seemingly fail to perform on SMC-Bench when applied out-of-the-box, sometimes at significantly trivial sparsity as low as 5%. By incorporating these well-thought and diverse tasks, SMC-Bench is designed to favor and encourage the development of more scalable and generalizable sparse algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge