Sortability of Time Series Data
Paper and Code
Jul 18, 2024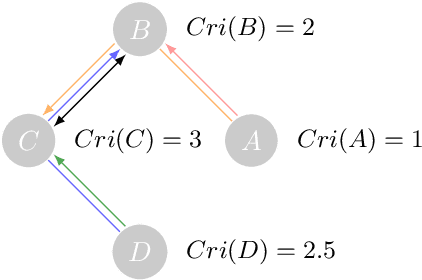
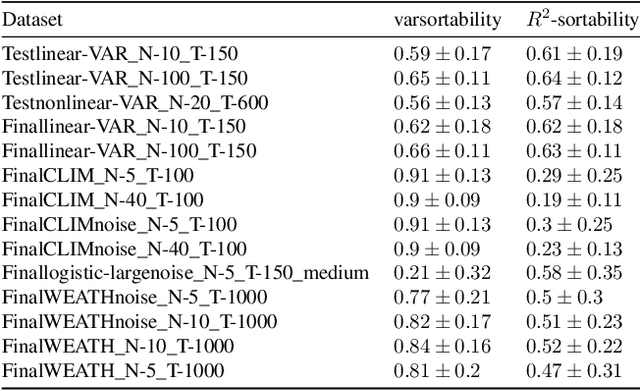
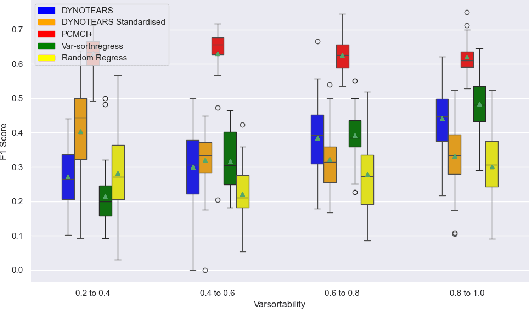
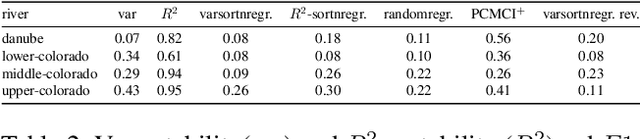
Evaluating the performance of causal discovery algorithms that aim to find causal relationships between time-dependent processes remains a challenging topic. In this paper, we show that certain characteristics of datasets, such as varsortability (Reisach et al. 2021) and $R^2$-sortability (Reisach et al. 2023), also occur in datasets for autocorrelated stationary time series. We illustrate this empirically using four types of data: simulated data based on SVAR models and Erd\H{o}s-R\'enyi graphs, the data used in the 2019 causality-for-climate challenge (Runge et al. 2019), real-world river stream datasets, and real-world data generated by the Causal Chamber of (Gamella et al. 2024). To do this, we adapt var- and $R^2$-sortability to time series data. We also investigate the extent to which the performance of score-based causal discovery methods goes hand in hand with high sortability. Arguably, our most surprising finding is that the investigated real-world datasets exhibit high varsortability and low $R^2$-sortability indicating that scales may carry a significant amount of causal information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge