Social-VRNN: One-Shot Multi-modal Trajectory Prediction for Interacting Pedestrians
Paper and Code
Oct 18, 2020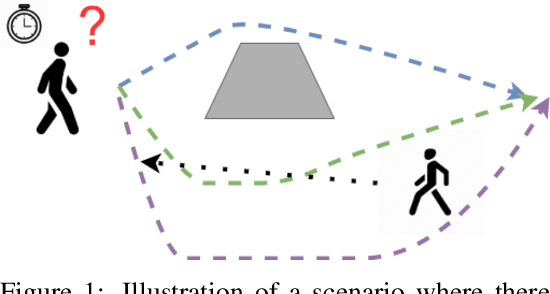
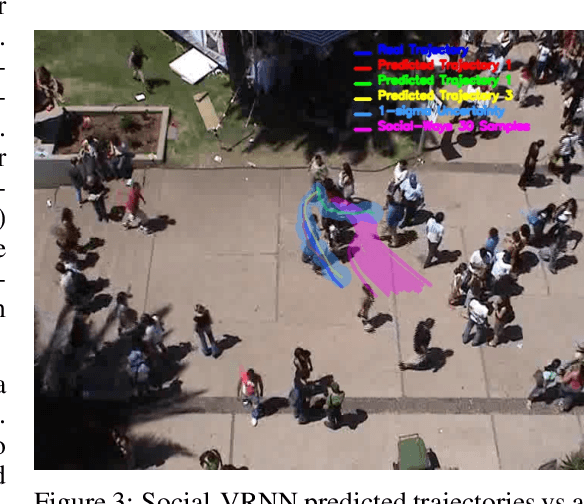
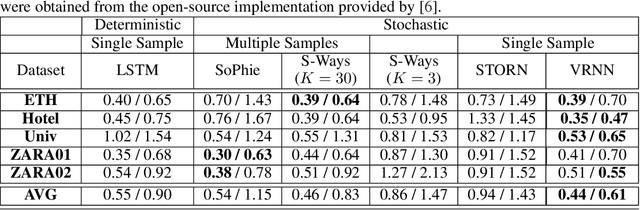


Prediction of human motions is key for safe navigation of autonomous robots among humans. In cluttered environments, several motion hypotheses may exist for a pedestrian, due to its interactions with the environment and other pedestrians. Previous works for estimating multiple motion hypotheses require a large number of samples which limits their applicability in real-time motion planning. In this paper, we present a variational learning approach for interaction-aware and multi-modal trajectory prediction based on deep generative neural networks. Our approach can achieve faster convergence and requires significantly fewer samples comparing to state-of-the-art methods. Experimental results on real and simulation data show that our model can effectively learn to infer different trajectories. We compare our method with three baseline approaches and present performance results demonstrating that our generative model can achieve higher accuracy for trajectory prediction by producing diverse trajectories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge