Social Cohesion in Autonomous Driving
Paper and Code
Aug 27, 2018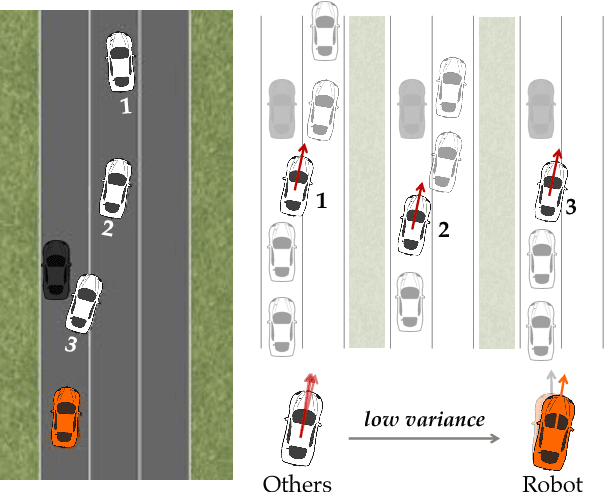

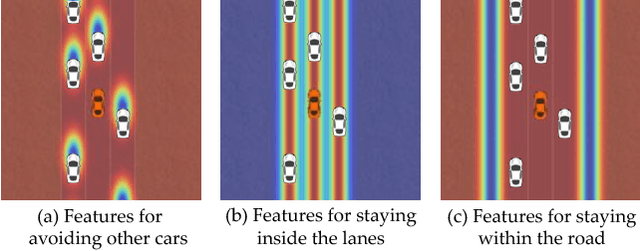
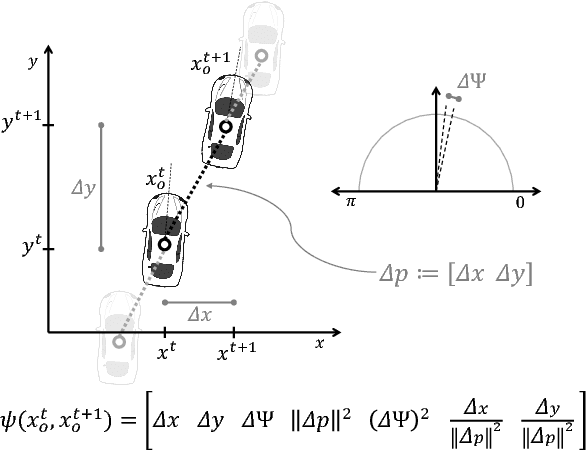
Autonomous cars can perform poorly for many reasons. They may have perception issues, incorrect dynamics models, be unaware of obscure rules of human traffic systems, or follow certain rules too conservatively. Regardless of the exact failure mode of the car, often human drivers around the car are behaving correctly. For example, even if the car does not know that it should pull over when an ambulance races by, other humans on the road will know and will pull over. We propose to make socially cohesive cars that leverage the behavior of nearby human drivers to act in ways that are safer and more socially acceptable. The simple intuition behind our algorithm is that if all the humans are consistently behaving in a particular way, then the autonomous car probably should too. We analyze the performance of our algorithm in a variety of scenarios and conduct a user study to assess people's attitudes towards socially cohesive cars. We find that people are surprisingly tolerant of mistakes that cohesive cars might make in order to get the benefits of driving in a car with a safer, or even just more socially acceptable behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge