Sketching sounds: an exploratory study on sound-shape associations
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2021
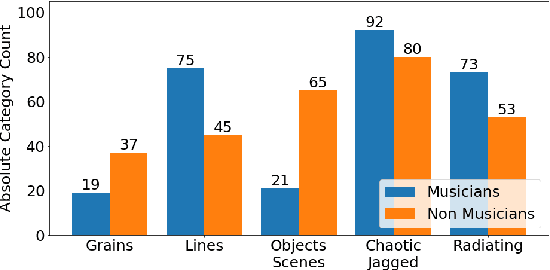
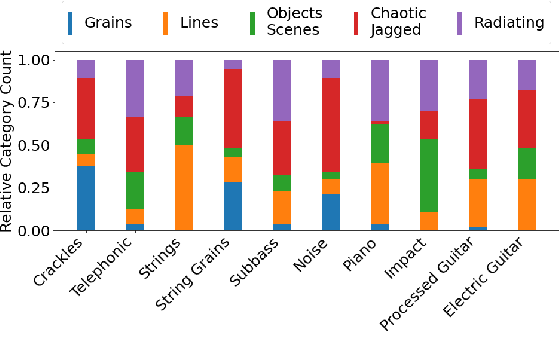
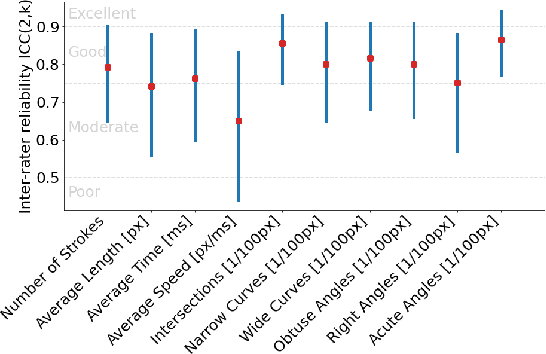
Sound synthesiser controls typically correspond to technical parameters of signal processing algorithms rather than intuitive sound descriptors that relate to human perception of sound. This makes it difficult to realise sound ideas in a straightforward way. Cross-modal mappings, for example between gestures and sound, have been suggested as a more intuitive control mechanism. A large body of research shows consistency in human associations between sounds and shapes. However, the use of drawings to drive sound synthesis has not been explored to its full extent. This paper presents an exploratory study that asked participants to sketch visual imagery of sounds with a monochromatic digital drawing interface, with the aim to identify different representational approaches and determine whether timbral sound characteristics can be communicated reliably through visual sketches. Results imply that the development of a synthesiser exploiting sound-shape associations is feasible, but a larger and more focused dataset is needed in followup studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge