Simultaneous Denoising and Motion Estimation for Low-dose Gated PET using a Siamese Adversarial Network with Gate-to-Gate Consistency Learning
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2020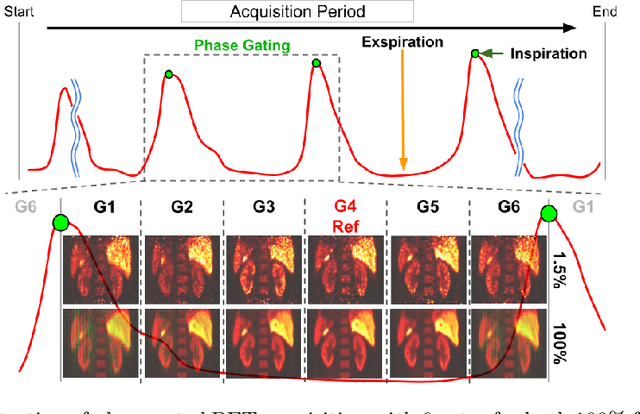
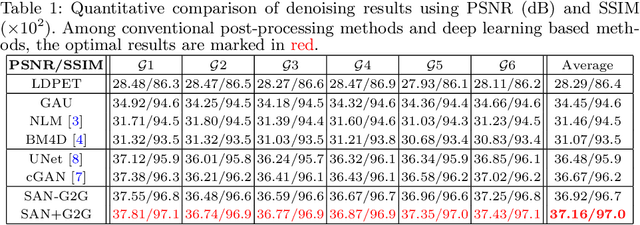
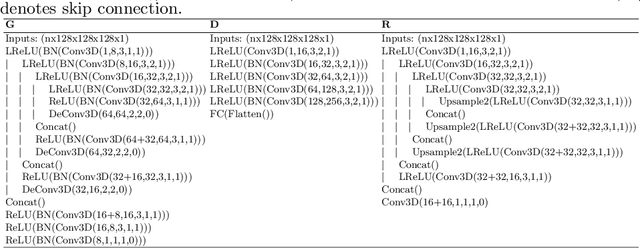
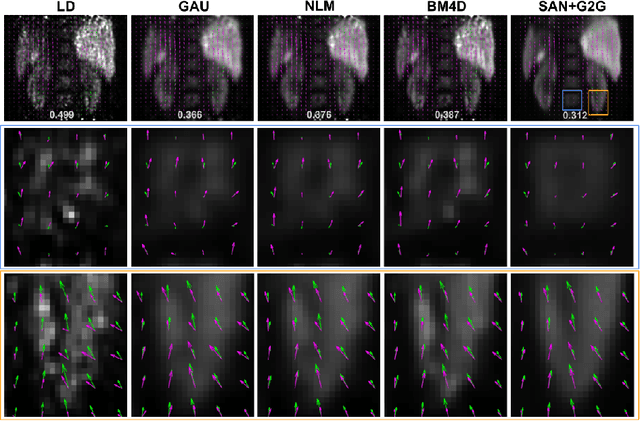
Gating is commonly used in PET imaging to reduce respiratory motion blurring and facilitate more sophisticated motion correction methods. In the applications of low dose PET, however, reducing injection dose causes increased noise and reduces signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), subsequently corrupting the motion estimation/correction steps, causing inferior image quality. To tackle these issues, we first propose a Siamese adversarial network (SAN) that can efficiently recover high dose gated image volume from low dose gated image volume. To ensure the appearance consistency between the recovered gated volumes, we then utilize a pre-trained motion estimation network incorporated into SAN that enables the constraint of gate-to-gate (G2G) consistency. With high-quality recovered gated volumes, gate-to-gate motion vectors can be simultaneously outputted from the motion estimation network. Comprehensive evaluations on a low dose gated PET dataset of 29 subjects demonstrate that our method can effectively recover the low dose gated PET volumes, with an average PSNR of 37.16 and SSIM of 0.97, and simultaneously generate robust motion estimation that could benefit subsequent motion corrections.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge