Signal Watermark on Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Oct 09, 2024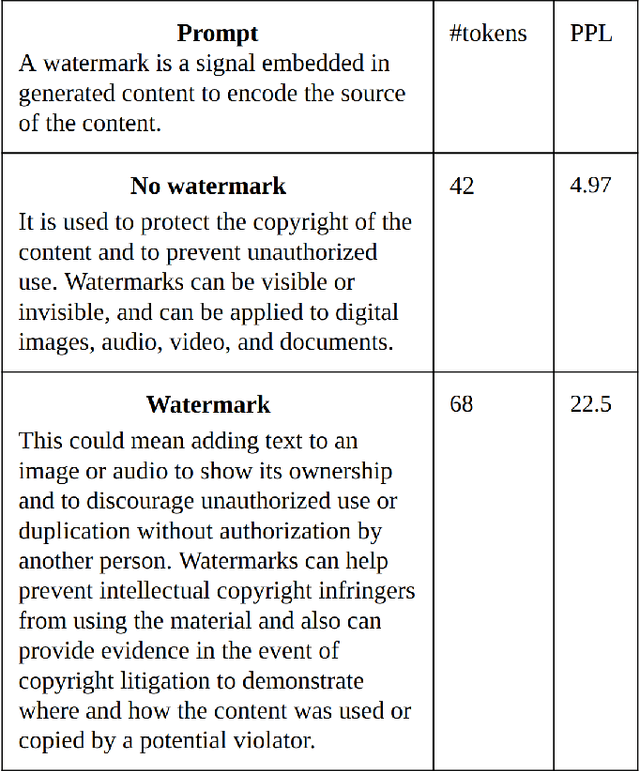

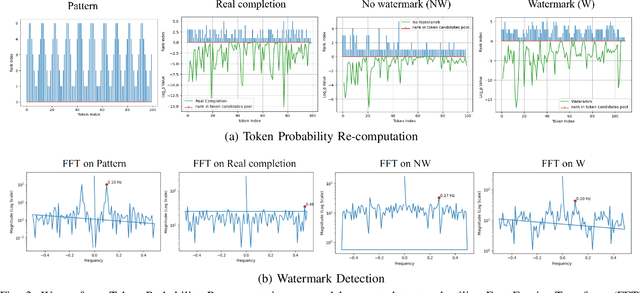
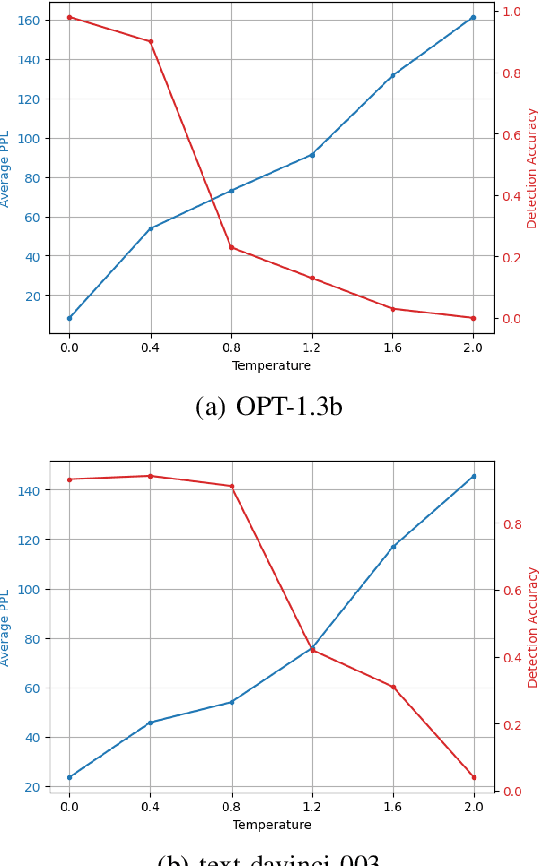
As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly sophisticated, they raise significant security concerns, including the creation of fake news and academic misuse. Most detectors for identifying model-generated text are limited by their reliance on variance in perplexity and burstiness, and they require substantial computational resources. In this paper, we proposed a watermarking method embedding a specific watermark into the text during its generation by LLMs, based on a pre-defined signal pattern. This technique not only ensures the watermark's invisibility to humans but also maintains the quality and grammatical integrity of model-generated text. We utilize LLMs and Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for token probability computation and detection of the signal watermark. The unique application of signal processing principles within the realm of text generation by LLMs allows for subtle yet effective embedding of watermarks, which do not compromise the quality or coherence of the generated text. Our method has been empirically validated across multiple LLMs, consistently maintaining high detection accuracy, even with variations in temperature settings during text generation. In the experiment of distinguishing between human-written and watermarked text, our method achieved an AUROC score of 0.97, significantly outperforming existing methods like GPTZero, which scored 0.64. The watermark's resilience to various attacking scenarios further confirms its robustness, addressing significant challenges in model-generated text authentication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge