ShuffleBlock: Shuffle to Regularize Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2021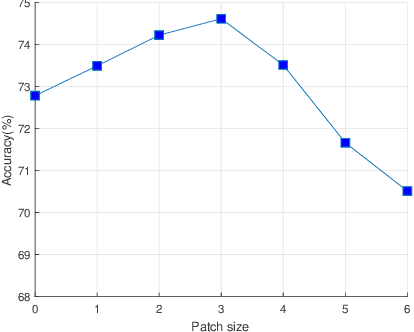

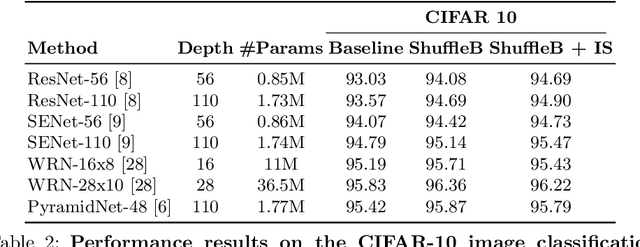
Deep neural networks have enormous representational power which leads them to overfit on most datasets. Thus, regularizing them is important in order to reduce overfitting and enhance their generalization capabilities. Recently, channel shuffle operation has been introduced for mixing channels in group convolutions in resource efficient networks in order to reduce memory and computations. This paper studies the operation of channel shuffle as a regularization technique in deep convolutional networks. We show that while random shuffling of channels during training drastically reduce their performance, however, randomly shuffling small patches between channels significantly improves their performance. The patches to be shuffled are picked from the same spatial locations in the feature maps such that a patch, when transferred from one channel to another, acts as structured noise for the later channel. We call this method "ShuffleBlock". The proposed ShuffleBlock module is easy to implement and improves the performance of several baseline networks on the task of image classification on CIFAR and ImageNet datasets. It also achieves comparable and in many cases better performance than many other regularization methods. We provide several ablation studies on selecting various hyperparameters of the ShuffleBlock module and propose a new scheduling method that further enhances its performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge