Short-term Load Forecasting with Deep Residual Networks
Paper and Code
May 30, 2018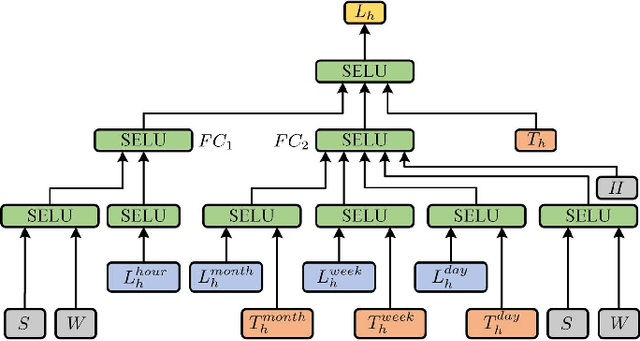
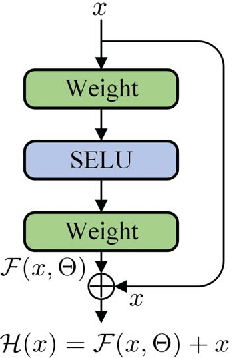
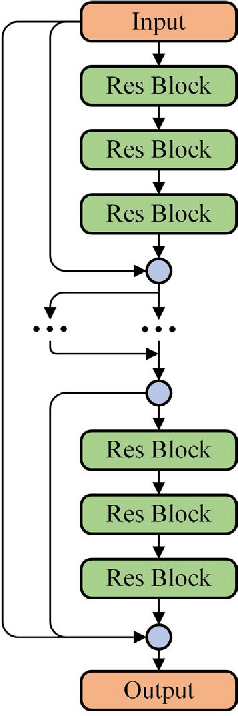
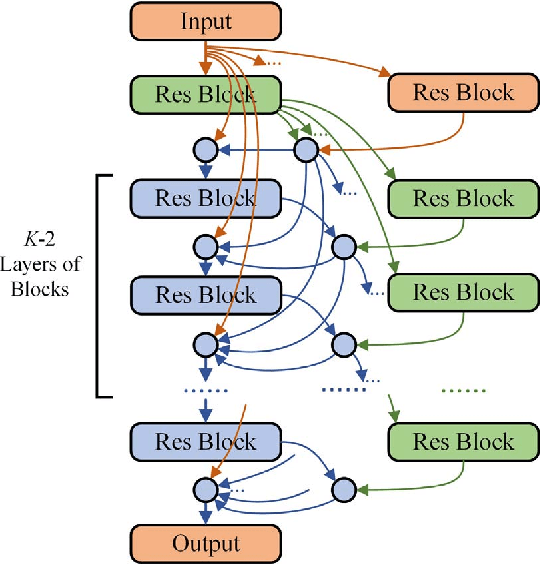
We present in this paper a model for forecasting short-term power loads based on deep residual networks. The proposed model is able to integrate domain knowledge and researchers' understanding of the task by virtue of different neural network building blocks. Specifically, a modified deep residual network is formulated to improve the forecast results. Further, a two-stage ensemble strategy is used to enhance the generalization capability of the proposed model. We also apply the proposed model to probabilistic load forecasting using Monte Carlo dropout. Three public datasets are used to prove the effectiveness of the proposed model. Multiple test cases and comparison with existing models show that the proposed model is able to provide accurate load forecasting results and has high generalization capability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge