SEN2DWATER: A Novel Multispectral and Multitemporal Dataset and Deep Learning Benchmark for Water Resources Analysis
Paper and Code
Jan 18, 2023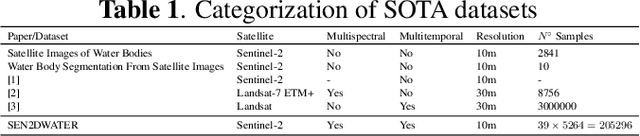
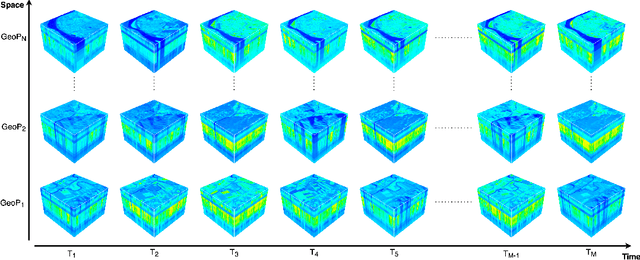
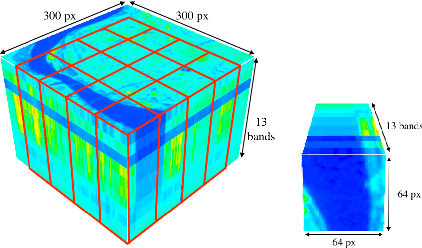
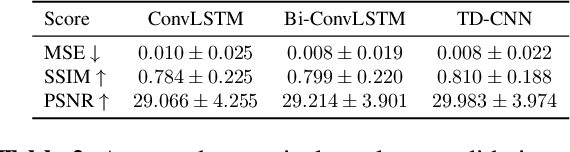
Climate change has caused disruption in certain weather patterns, leading to extreme weather events like flooding and drought in different parts of the world. In this paper, we propose machine learning methods for analyzing changes in water resources over a time period of six years, by focusing on lakes and rivers in Italy and Spain. Additionally, we release open-access code to enable the expansion of the study to any region of the world. We create a novel multispectral and multitemporal dataset, SEN2DWATER, which is freely accessible on GitHub. We introduce suitable indices to monitor changes in water resources, and benchmark the new dataset on three different deep learning frameworks: Convolutional Long Short Term Memory (ConvLSTM), Bidirectional ConvLSTM, and Time Distributed Convolutional Neural Networks (TD-CNNs). Future work exploring the many potential applications of this research is also discussed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge