Semantic Sensing and Planning for Human-Robot Collaboration in Uncertain Environments
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2021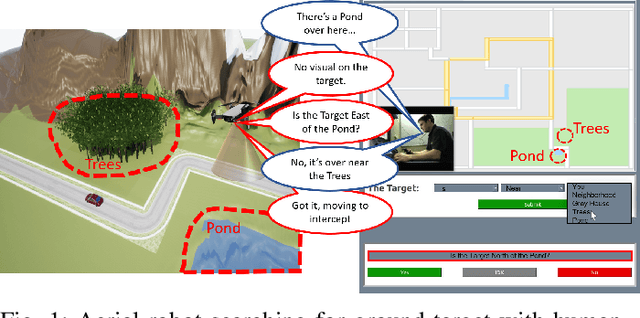
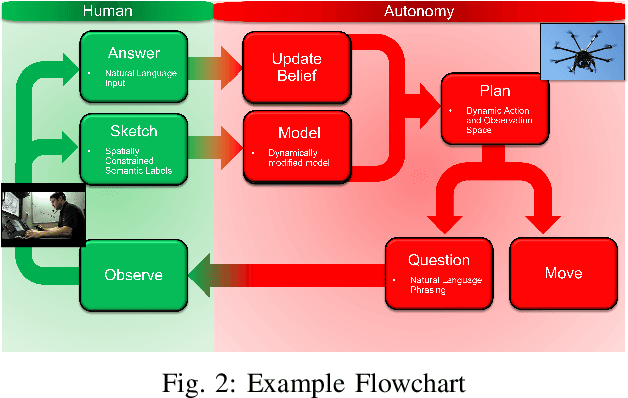
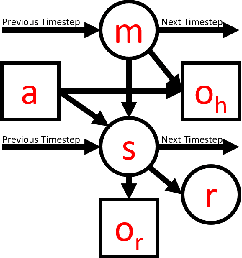
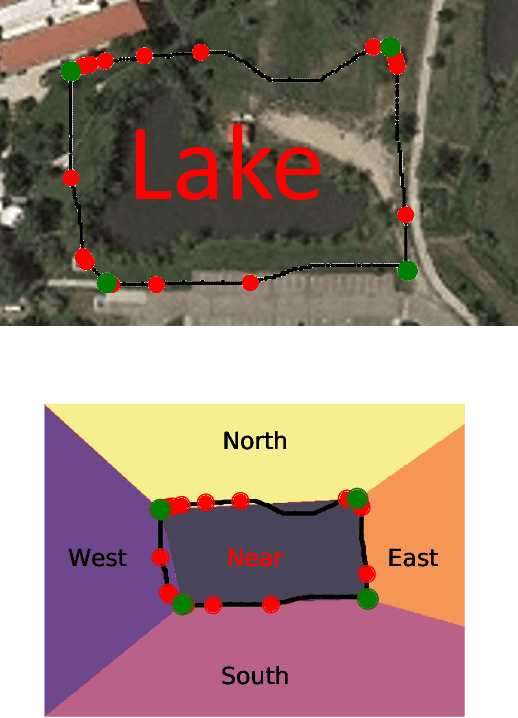
Autonomous robots can benefit greatly from human-provided semantic characterizations of uncertain task environments and states. However, the development of integrated strategies which let robots model, communicate, and act on such soft data remains challenging. Here, a framework is presented for active semantic sensing and planning in human-robot teams which addresses these gaps by formally combining the benefits of online sampling-based POMDP policies, multi-modal semantic interaction, and Bayesian data fusion. This approach lets humans opportunistically impose model structure and extend the range of semantic soft data in uncertain environments by sketching and labeling arbitrary landmarks across the environment. Dynamic updating of the environment while searching for a mobile target allows robotic agents to actively query humans for novel and relevant semantic data, thereby improving beliefs of unknown environments and target states for improved online planning. Target search simulations show significant improvements in time and belief state estimates required for interception versus conventional planning based solely on robotic sensing. Human subject studies demonstrate a average doubling in dynamic target capture rate compared to the lone robot case, employing reasoning over a range of user characteristics and interaction modalities. Video of interaction can be found at https://youtu.be/Eh-82ZJ1o4I.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge