Self-Supervised Learning for Pre-training Capsule Networks: Overcoming Medical Imaging Dataset Challenges
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2025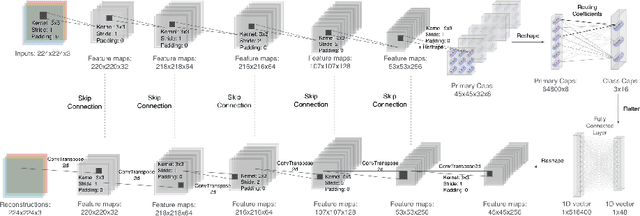
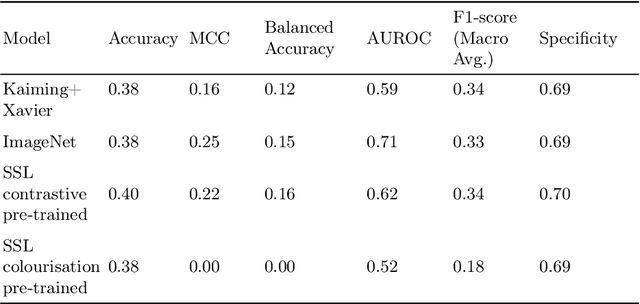
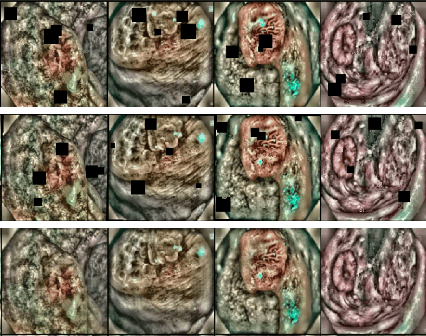
Deep learning techniques are increasingly being adopted in diagnostic medical imaging. However, the limited availability of high-quality, large-scale medical datasets presents a significant challenge, often necessitating the use of transfer learning approaches. This study investigates self-supervised learning methods for pre-training capsule networks in polyp diagnostics for colon cancer. We used the PICCOLO dataset, comprising 3,433 samples, which exemplifies typical challenges in medical datasets: small size, class imbalance, and distribution shifts between data splits. Capsule networks offer inherent interpretability due to their architecture and inter-layer information routing mechanism. However, their limited native implementation in mainstream deep learning frameworks and the lack of pre-trained versions pose a significant challenge. This is particularly true if aiming to train them on small medical datasets, where leveraging pre-trained weights as initial parameters would be beneficial. We explored two auxiliary self-supervised learning tasks, colourisation and contrastive learning, for capsule network pre-training. We compared self-supervised pre-trained models against alternative initialisation strategies. Our findings suggest that contrastive learning and in-painting techniques are suitable auxiliary tasks for self-supervised learning in the medical domain. These techniques helped guide the model to capture important visual features that are beneficial for the downstream task of polyp classification, increasing its accuracy by 5.26% compared to other weight initialisation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge