Self-Supervised Learning for 3D Medical Image Analysis using 3D SimCLR and Monte Carlo Dropout
Paper and Code
Oct 01, 2021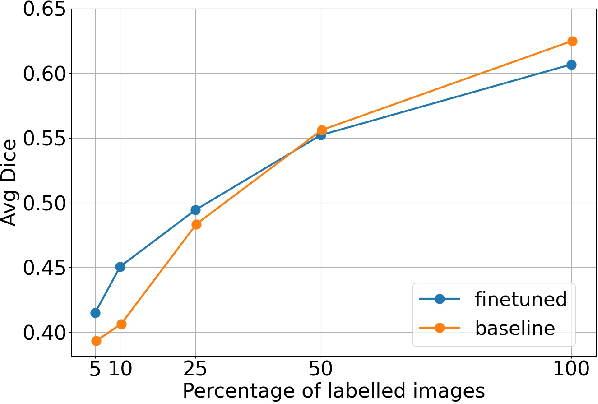
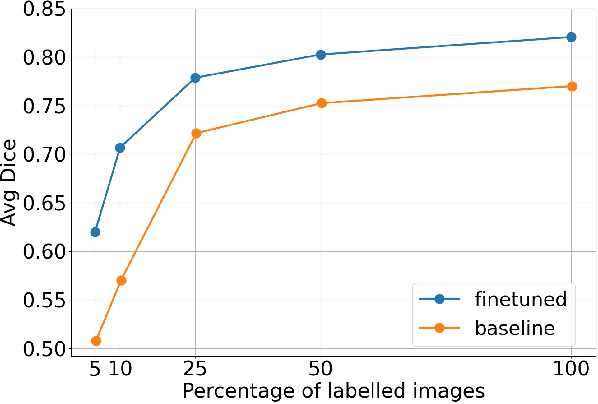
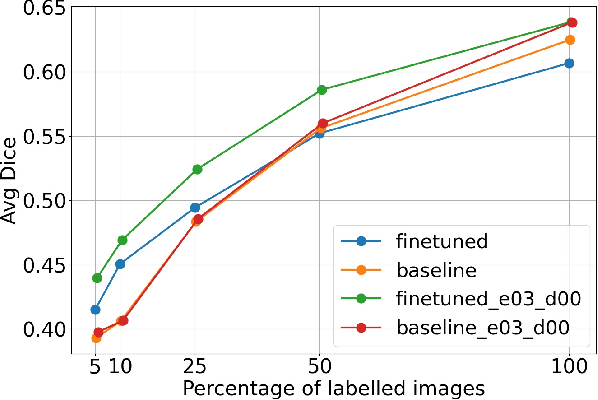
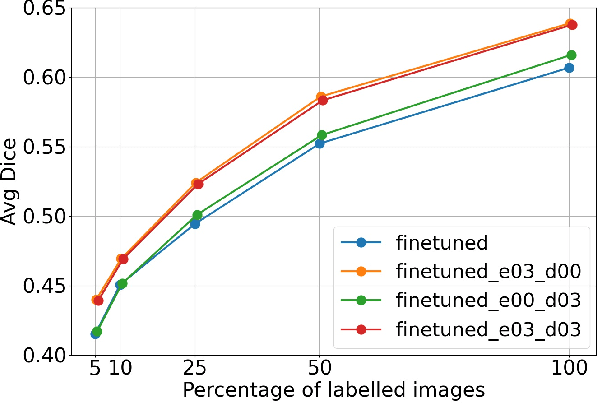
Self-supervised learning methods can be used to learn meaningful representations from unlabeled data that can be transferred to supervised downstream tasks to reduce the need for labeled data. In this paper, we propose a 3D self-supervised method that is based on the contrastive (SimCLR) method. Additionally, we show that employing Bayesian neural networks (with Monte-Carlo Dropout) during the inference phase can further enhance the results on the downstream tasks. We showcase our models on two medical imaging segmentation tasks: i) Brain Tumor Segmentation from 3D MRI, ii) Pancreas Tumor Segmentation from 3D CT. Our experimental results demonstrate the benefits of our proposed methods in both downstream data-efficiency and performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge