Segmentation of structural parts of rosebush plants with 3D point-based deep learning methods
Paper and Code
Dec 21, 2020
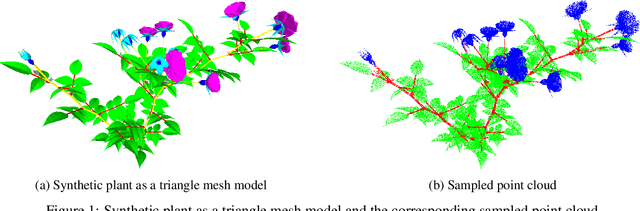
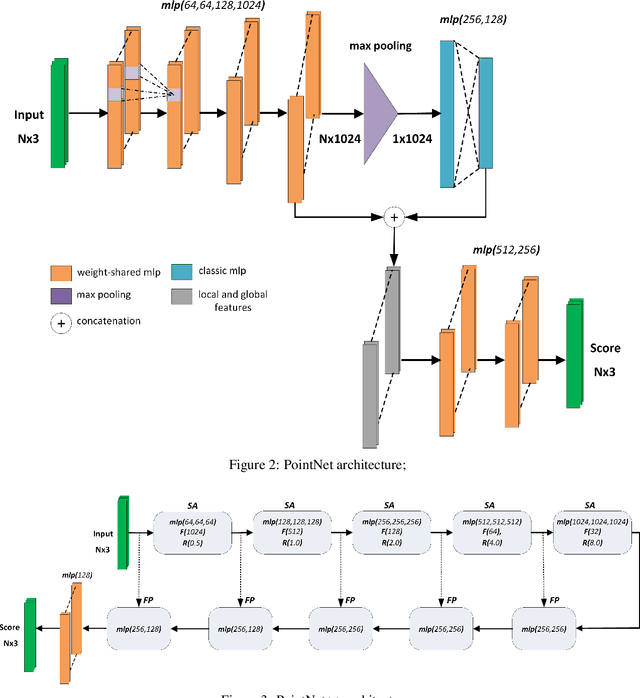
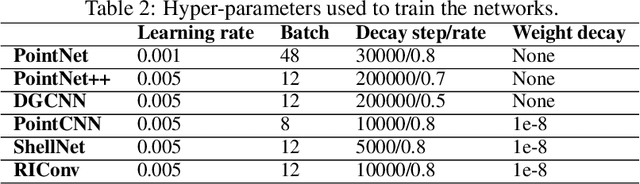
Segmentation of structural parts of 3D models of plants is an important step for plant phenotyping, especially for monitoring architectural and morphological traits. This work introduces a benchmark for assessing the performance of 3D point-based deep learning methods on organ segmentation of 3D plant models, specifically rosebush models. Six recent deep learning architectures that segment 3D point clouds into semantic parts were adapted and compared. The methods were tested on the ROSE-X data set, containing fully annotated 3D models of real rosebush plants. The contribution of incorporating synthetic 3D models generated through Lindenmayer systems into training data was also investigated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge