Segmentation-based Information Extraction and Amalgamation in Fundus Images for Glaucoma Detection
Paper and Code
Sep 23, 2022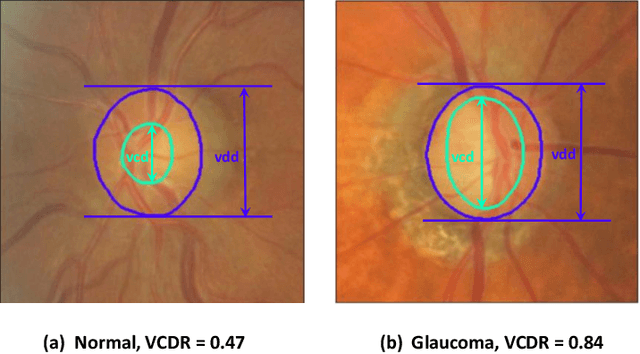

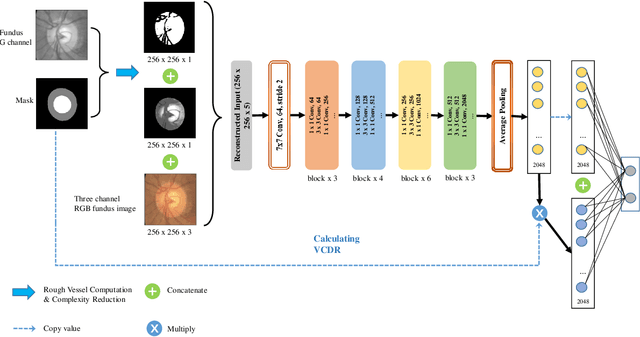

Glaucoma is a severe blinding disease, for which automatic detection methods are urgently needed to alleviate the scarcity of ophthalmologists. Many works have proposed to employ deep learning methods that involve the segmentation of optic disc and cup for glaucoma detection, in which the segmentation process is often considered merely as an upstream sub-task. The relationship between fundus images and segmentation masks in terms of joint decision-making in glaucoma assessment is rarely explored. We propose a novel segmentation-based information extraction and amalgamation method for the task of glaucoma detection, which leverages the robustness of segmentation masks without disregarding the rich information in the original fundus images. Experimental results on both private and public datasets demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms all models that utilize solely either fundus images or masks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge