ScoreCAM GNN: une explication optimale des réseaux profonds sur graphes
Paper and Code
Jul 26, 2022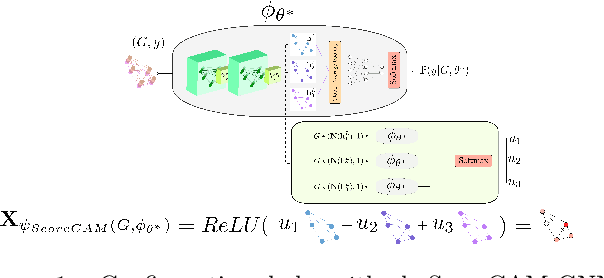
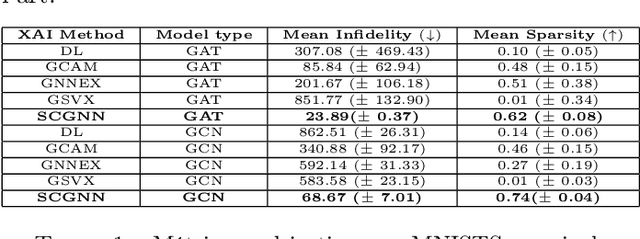
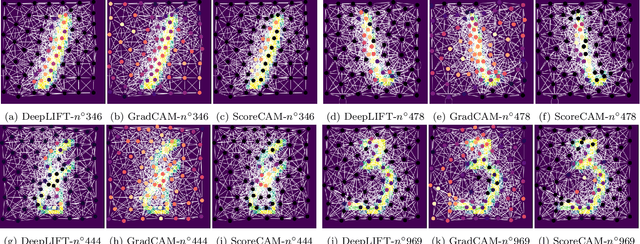
The explainability of deep networks is becoming a central issue in the deep learning community. It is the same for learning on graphs, a data structure present in many real world problems. In this paper, we propose a method that is more optimal, lighter, consistent and better exploits the topology of the evaluated graph than the state-of-the-art methods.
* in French language. XXVIIIe Colloque GRETSI - Traitement du Signal et
des Images, Sep 2022, Nancy, France
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge