Scaling Marginalized Importance Sampling to High-Dimensional State-Spaces via State Abstraction
Paper and Code
Dec 14, 2022
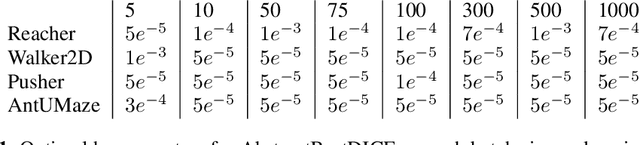
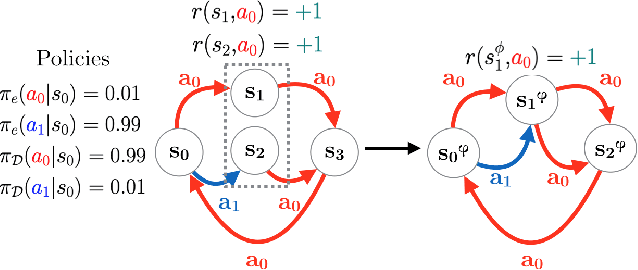
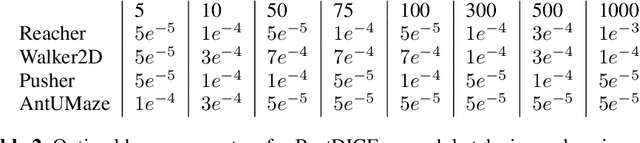
We consider the problem of off-policy evaluation (OPE) in reinforcement learning (RL), where the goal is to estimate the performance of an evaluation policy, $\pi_e$, using a fixed dataset, $\mathcal{D}$, collected by one or more policies that may be different from $\pi_e$. Current OPE algorithms may produce poor OPE estimates under policy distribution shift i.e., when the probability of a particular state-action pair occurring under $\pi_e$ is very different from the probability of that same pair occurring in $\mathcal{D}$ (Voloshin et al. 2021, Fu et al. 2021). In this work, we propose to improve the accuracy of OPE estimators by projecting the high-dimensional state-space into a low-dimensional state-space using concepts from the state abstraction literature. Specifically, we consider marginalized importance sampling (MIS) OPE algorithms which compute state-action distribution correction ratios to produce their OPE estimate. In the original ground state-space, these ratios may have high variance which may lead to high variance OPE. However, we prove that in the lower-dimensional abstract state-space the ratios can have lower variance resulting in lower variance OPE. We then highlight the challenges that arise when estimating the abstract ratios from data, identify sufficient conditions to overcome these issues, and present a minimax optimization problem whose solution yields these abstract ratios. Finally, our empirical evaluation on difficult, high-dimensional state-space OPE tasks shows that the abstract ratios can make MIS OPE estimators achieve lower mean-squared error and more robust to hyperparameter tuning than the ground ratios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge