Say Anything: Automatic Semantic Infelicity Detection in L2 English Indefinite Pronouns
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2019
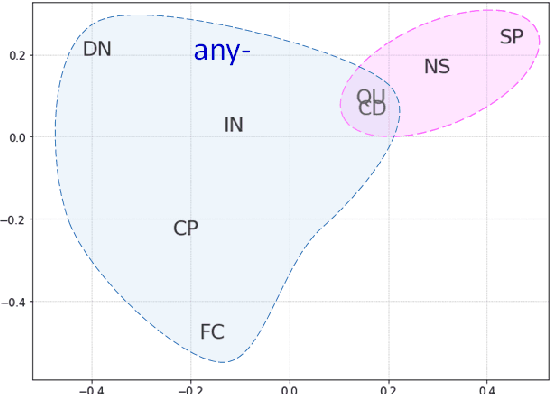
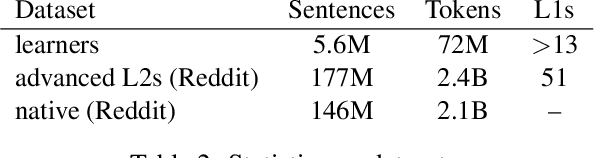
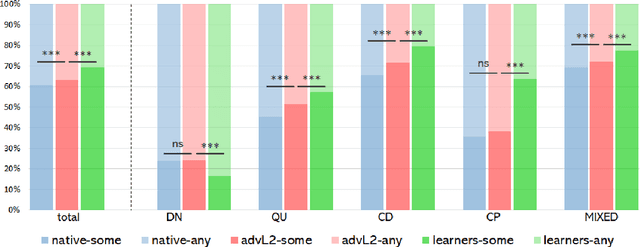
Computational research on error detection in second language speakers has mainly addressed clear grammatical anomalies typical to learners at the beginner-to-intermediate level. We focus instead on acquisition of subtle semantic nuances of English indefinite pronouns by non-native speakers at varying levels of proficiency. We first lay out theoretical, linguistically motivated hypotheses, and supporting empirical evidence on the nature of the challenges posed by indefinite pronouns to English learners. We then suggest and evaluate an automatic approach for detection of atypical usage patterns, demonstrating that deep learning architectures are promising for this task involving nuanced semantic anomalies.
* 10 pages, CoNLL2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge