SAVE: Segment Audio-Visual Easy way using Segment Anything Model
Paper and Code
Jul 02, 2024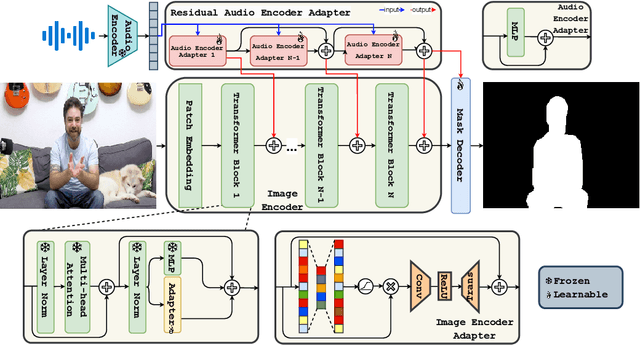
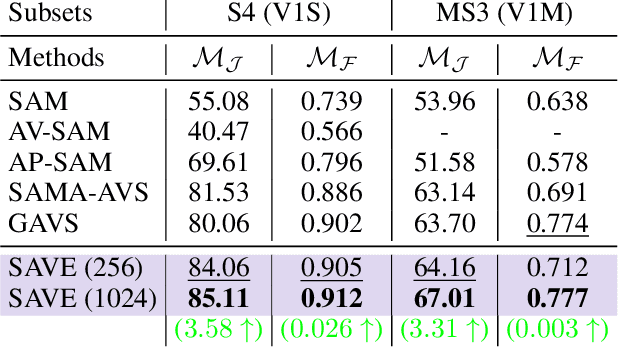
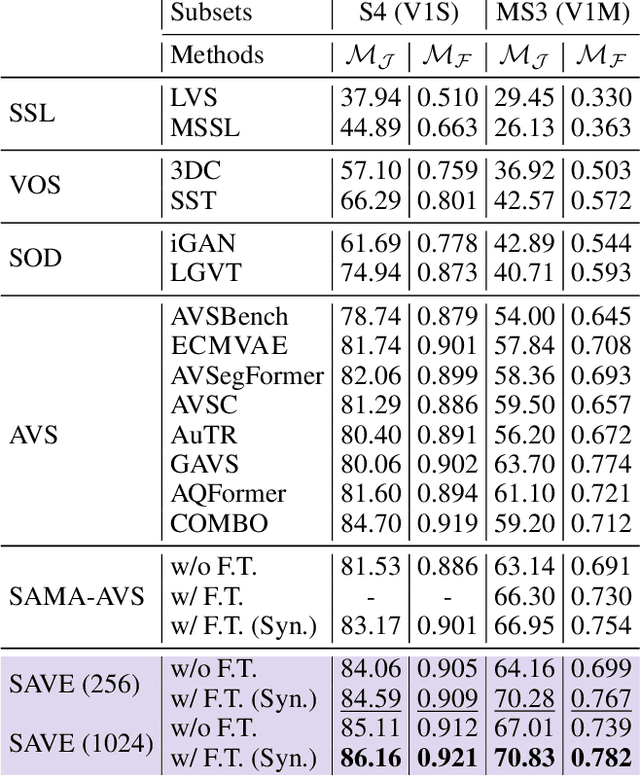
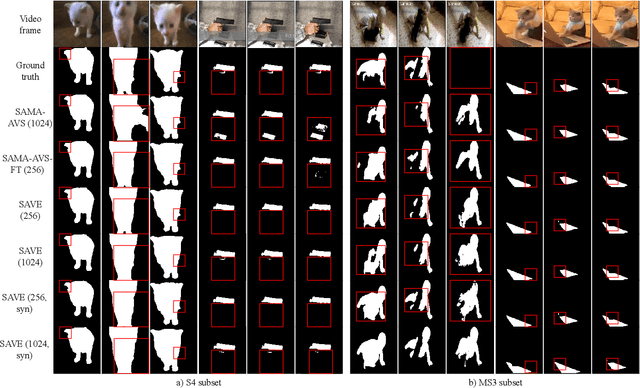
The primary aim of Audio-Visual Segmentation (AVS) is to precisely identify and locate auditory elements within visual scenes by accurately predicting segmentation masks at the pixel level. Achieving this involves comprehensively considering data and model aspects to address this task effectively. This study presents a lightweight approach, SAVE, which efficiently adapts the pre-trained segment anything model (SAM) to the AVS task. By incorporating an image encoder adapter into the transformer blocks to better capture the distinct dataset information and proposing a residual audio encoder adapter to encode the audio features as a sparse prompt, our proposed model achieves effective audio-visual fusion and interaction during the encoding stage. Our proposed method accelerates the training and inference speed by reducing the input resolution from 1024 to 256 pixels while achieving higher performance compared with the previous SOTA. Extensive experimentation validates our approach, demonstrating that our proposed model outperforms other SOTA methods significantly. Moreover, leveraging the pre-trained model on synthetic data enhances performance on real AVSBench data, achieving 84.59 mIoU on the S4 (V1S) subset and 70.28 mIoU on the MS3 (V1M) set with only 256 pixels for input images. This increases up to 86.16 mIoU on the S4 (V1S) and 70.83 mIoU on the MS3 (V1M) with inputs of 1024 pixels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge