Salted Inference: Enhancing Privacy while Maintaining Efficiency of Split Inference in Mobile Computing
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2023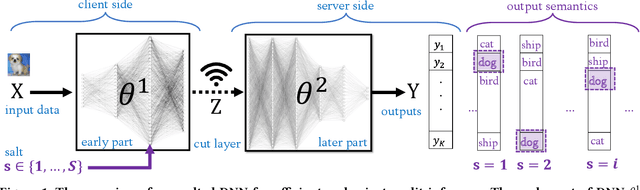


Split inference partitions a deep neural network (DNN) to run the early part at the edge and the later part in the cloud. This meets two key requirements for on-device machine learning: input privacy and compute efficiency. Still, an open question in split inference is output privacy, given that the output of a DNN is visible to the cloud. While encrypted computing can protect output privacy, it mandates extensive computation and communication resources. In this paper, we introduce "Salted DNNs": a novel method that lets clients control the semantic interpretation of DNN output at inference time while maintaining accuracy and efficiency very close to that of a standard DNN. Experimental evaluations conducted on both image and sensor data show that Salted DNNs achieve classification accuracy very close to standard DNNs, particularly when the salted layer is positioned within the early part to meet the requirements of split inference. Our method is general and can be applied to various DNNs. We open-source our code and results, as a benchmark for future studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge