Robust Stuttering Detection via Multi-task and Adversarial Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2022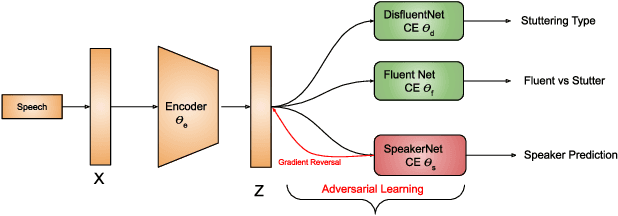
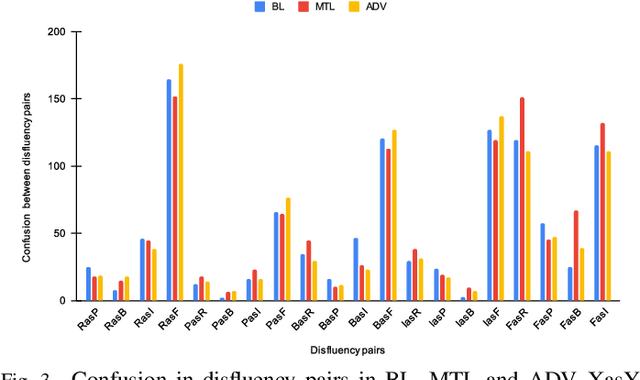
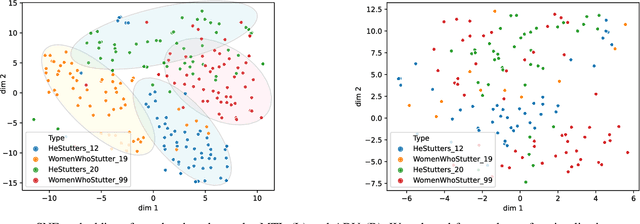
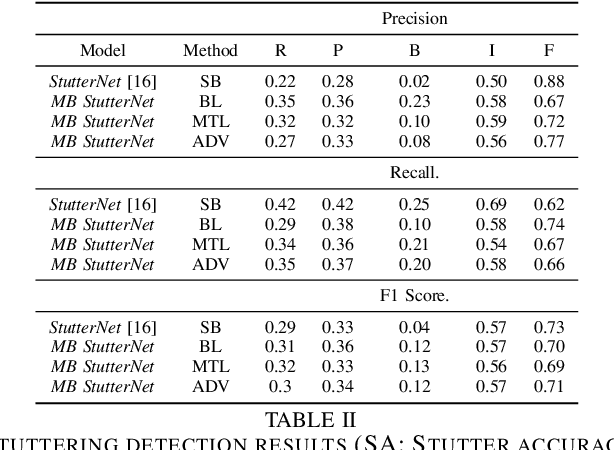
By automatic detection and identification of stuttering, speech pathologists can track the progression of disfluencies of persons who stutter (PWS). In this paper, we investigate the impact of multi-task (MTL) and adversarial learning (ADV) to learn robust stutter features. This is the first-ever preliminary study where MTL and ADV have been employed in stuttering identification (SI). We evaluate our system on the SEP-28k stuttering dataset consisting of 20 hours (approx) of data from 385 podcasts. Our methods show promising results and outperform the baseline in various disfluency classes. We achieve up to 10%, 6.78%, and 2% improvement in repetitions, blocks, and interjections respectively over the baseline.
* Under Review in European Signal Processing Conference 2022
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge