Robust sketching for multiple square-root LASSO problems
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2014
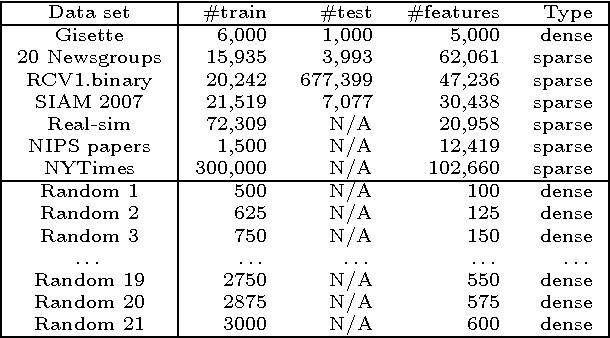

Many learning tasks, such as cross-validation, parameter search, or leave-one-out analysis, involve multiple instances of similar problems, each instance sharing a large part of learning data with the others. We introduce a robust framework for solving multiple square-root LASSO problems, based on a sketch of the learning data that uses low-rank approximations. Our approach allows a dramatic reduction in computational effort, in effect reducing the number of observations from $m$ (the number of observations to start with) to $k$ (the number of singular values retained in the low-rank model), while not sacrificing---sometimes even improving---the statistical performance. Theoretical analysis, as well as numerical experiments on both synthetic and real data, illustrate the efficiency of the method in large scale applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge