Robust Scatterer Number Density Segmentation of Ultrasound Images
Paper and Code
Jan 16, 2022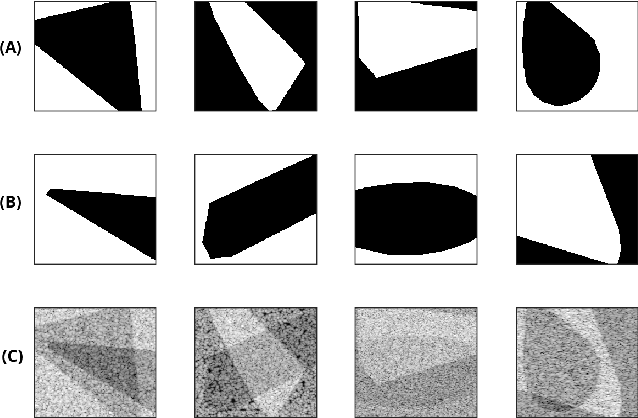
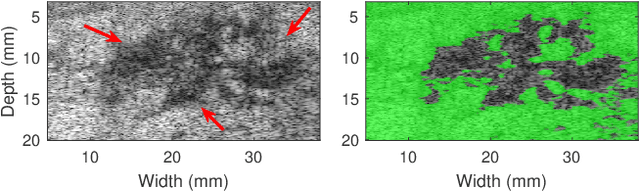
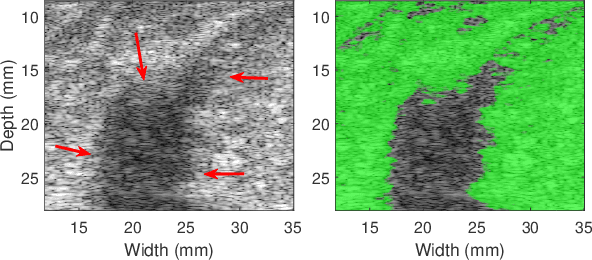
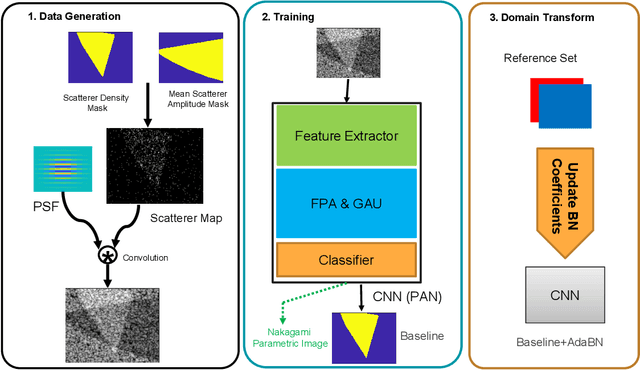
Quantitative UltraSound (QUS) aims to reveal information about the tissue microstructure using backscattered echo signals from clinical scanners. Among different QUS parameters, scatterer number density is an important property that can affect estimation of other QUS parameters. Scatterer number density can be classified into high or low scatterer densities. If there are more than 10 scatterers inside the resolution cell, the envelope data is considered as Fully Developed Speckle (FDS) and otherwise, as Under Developed Speckle (UDS). In conventional methods, the envelope data is divided into small overlapping windows (a strategy here we refer to as patching), and statistical parameters such as SNR and skewness are employed to classify each patch of envelope data. However, these parameters are system dependent meaning that their distribution can change by the imaging settings and patch size. Therefore, reference phantoms which have known scatterer number density are imaged with the same imaging settings to mitigate system dependency. In this paper, we aim to segment regions of ultrasound data without any patching. A large dataset is generated which has different shapes of scatterer number density and mean scatterer amplitude using a fast simulation method. We employ a convolutional neural network (CNN) for the segmentation task and investigate the effect of domain shift when the network is tested on different datasets with different imaging settings. Nakagami parametric image is employed for the multi-task learning to improve the performance. Furthermore, inspired by the reference phantom methods in QUS, A domain adaptation stage is proposed which requires only two frames of data from FDS and UDS classes. We evaluate our method for different experimental phantoms and in vivo data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge