Robust quantum minimum finding with an application to hypothesis selection
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2020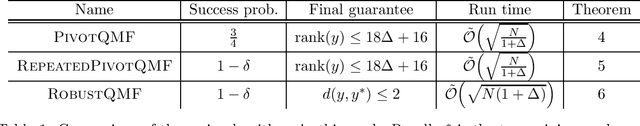
We consider the problem of finding the minimum element in a list of length $N$ using a noisy comparator. The noise is modelled as follows: given two elements to compare, if the values of the elements differ by at least $\alpha$ by some metric defined on the elements, then the comparison will be made correctly; if the values of the elements are closer than $\alpha$, the outcome of the comparison is not subject to any guarantees. We demonstrate a quantum algorithm for noisy quantum minimum-finding that preserves the quadratic speedup of the noiseless case: our algorithm runs in time $\tilde O(\sqrt{N (1+\Delta)})$, where $\Delta$ is an upper-bound on the number of elements within the interval $\alpha$, and outputs a good approximation of the true minimum with high probability. Our noisy comparator model is motivated by the problem of hypothesis selection, where given a set of $N$ known candidate probability distributions and samples from an unknown target distribution, one seeks to output some candidate distribution $O(\varepsilon)$-close to the unknown target. Much work on the classical front has been devoted to speeding up the run time of classical hypothesis selection from $O(N^2)$ to $O(N)$, in part by using statistical primitives such as the Scheff\'{e} test. Assuming a quantum oracle generalization of the classical data access and applying our noisy quantum minimum-finding algorithm, we take this run time into the sublinear regime. The final expected run time is $\tilde O( \sqrt{N(1+\Delta)})$, with the same $O(\log N)$ sample complexity from the unknown distribution as the classical algorithm. We expect robust quantum minimum-finding to be a useful building block for algorithms in situations where the comparator (which may be another quantum or classical algorithm) is resolution-limited or subject to some uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge