Road Detection via On--line Label Transfer
Paper and Code
Dec 10, 2014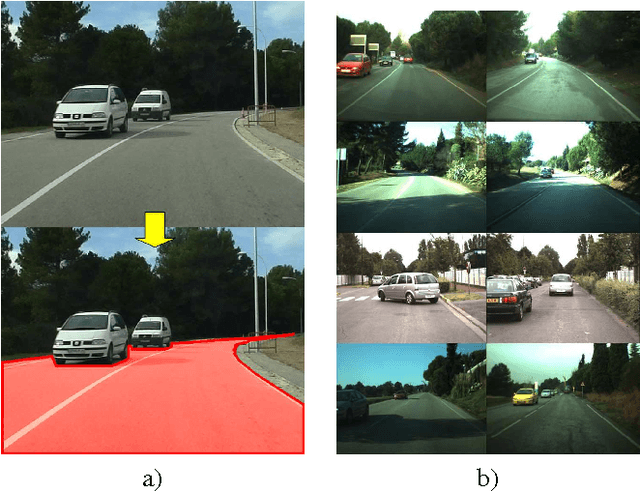
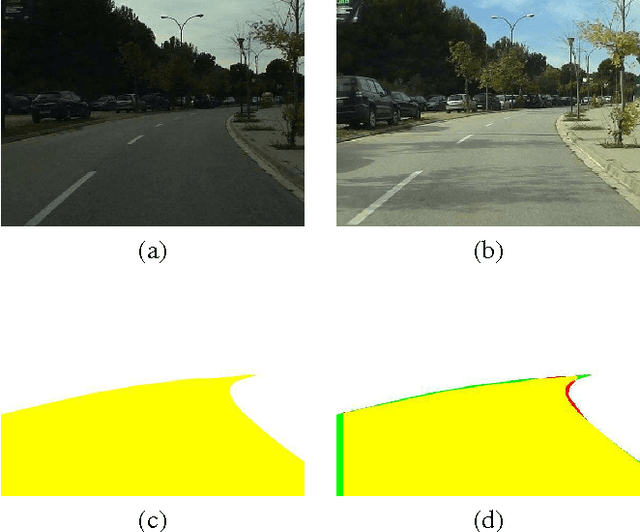
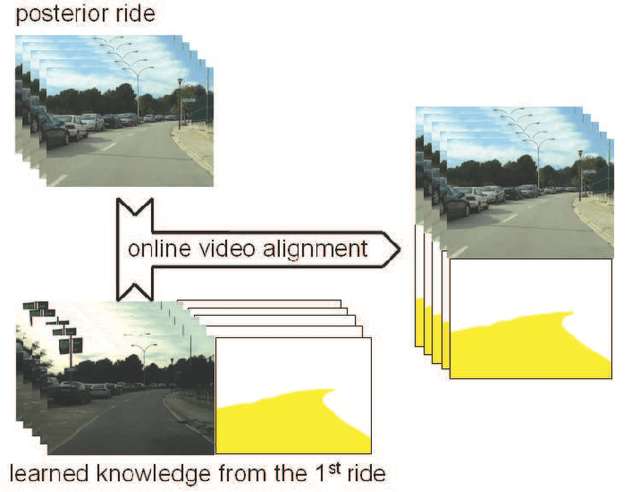
Vision-based road detection is an essential functionality for supporting advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) such as road following and vehicle and pedestrian detection. The major challenges of road detection are dealing with shadows and lighting variations and the presence of other objects in the scene. Current road detection algorithms characterize road areas at pixel level and group pixels accordingly. However, these algorithms fail in presence of strong shadows and lighting variations. Therefore, we propose a road detection algorithm based on video alignment. The key idea of the algorithm is to exploit the similarities occurred when a vehicle follows the same trajectory more than once. In this way, road areas are learned in a first ride and then, this road knowledge is used to infer areas depicting drivable road surfaces in subsequent rides. Two different experiments are conducted to validate the proposal on different video sequences taken at different scenarios and different daytime. The former aims to perform on-line road detection. The latter aims to perform off-line road detection and is applied to automatically generate the ground-truth necessary to validate road detection algorithms. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations prove that the proposed algorithm is a valid road detection approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge