ReWiS: Reliable Wi-Fi Sensing Through Few-Shot Multi-Antenna Multi-Receiver CSI Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 03, 2022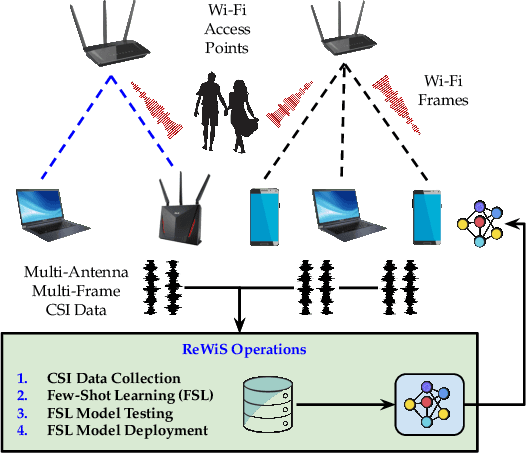
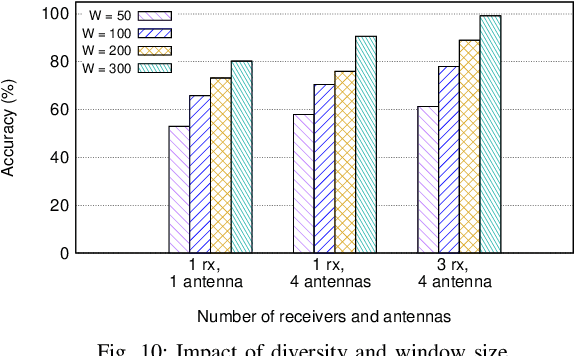
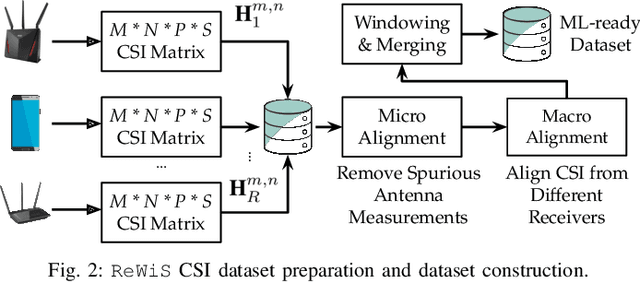
Thanks to the ubiquitousness of Wi-Fi access points and devices, Wi-Fi sensing enables transformative applications in remote health care, security, and surveillance. Existing work has explored the usage of machine learning on channel state information (CSI) computed from Wi-Fi packets to classify events of interest. However, most of these algorithms require a significant amount of data collection, as well as extensive computational power for additional CSI feature extraction. Moreover, the majority of these models suffer from poor accuracy when tested in a new/untrained environment. In this paper, we propose ReWiS, a novel framework for robust and environment-independent Wi-Fi sensing. The key innovation of ReWiS is to leverage few-shot learning (FSL) as the inference engine, which (i) reduces the need for extensive data collection and application-specific feature extraction; (ii) can rapidly generalize to new tasks by leveraging only a few new samples. We prototype ReWiS using off-the-shelf Wi-Fi equipment and showcase its performance by considering a compelling use case of human activity recognition. Thus, we perform an extensive data collection campaign in three different propagation environments with two human subjects. We evaluate the impact of each diversity component on the performance and compare ReWiS with a traditional convolutional neural network (CNN) approach. Experimental results show that ReWiS improves the performance by about 40% with respect to existing single-antenna low-resolution approaches. Moreover, when compared to a CNN-based approach, ReWiS shows a 35% more accuracy and less than 10% drop in accuracy when tested in different environments, while the CNN drops by more than 45%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge