Reward-Sharing Relational Networks in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning as a Framework for Emergent Behavior
Paper and Code
Jul 14, 2022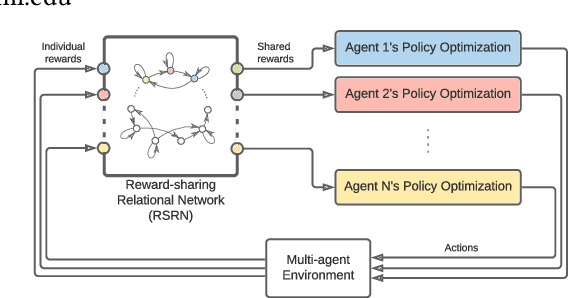
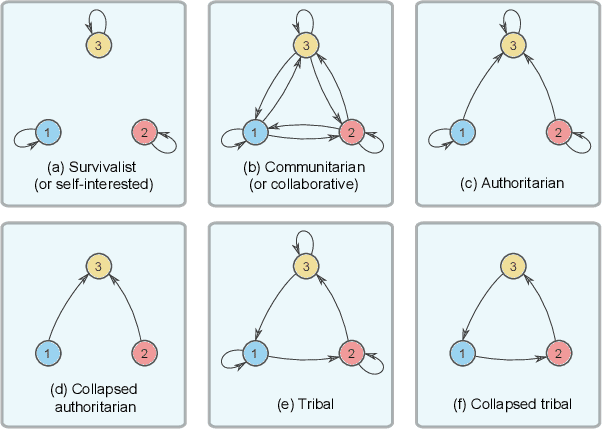
In this work, we integrate `social' interactions into the MARL setup through a user-defined relational network and examine the effects of agent-agent relations on the rise of emergent behaviors. Leveraging insights from sociology and neuroscience, our proposed framework models agent relationships using the notion of Reward-Sharing Relational Networks (RSRN), where network edge weights act as a measure of how much one agent is invested in the success of (or `cares about') another. We construct relational rewards as a function of the RSRN interaction weights to collectively train the multi-agent system via a multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithm. The performance of the system is tested for a 3-agent scenario with different relational network structures (e.g., self-interested, communitarian, and authoritarian networks). Our results indicate that reward-sharing relational networks can significantly influence learned behaviors. We posit that RSRN can act as a framework where different relational networks produce distinct emergent behaviors, often analogous to the intuited sociological understanding of such networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge