Retrieval-Augmented Purifier for Robust LLM-Empowered Recommendation
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2025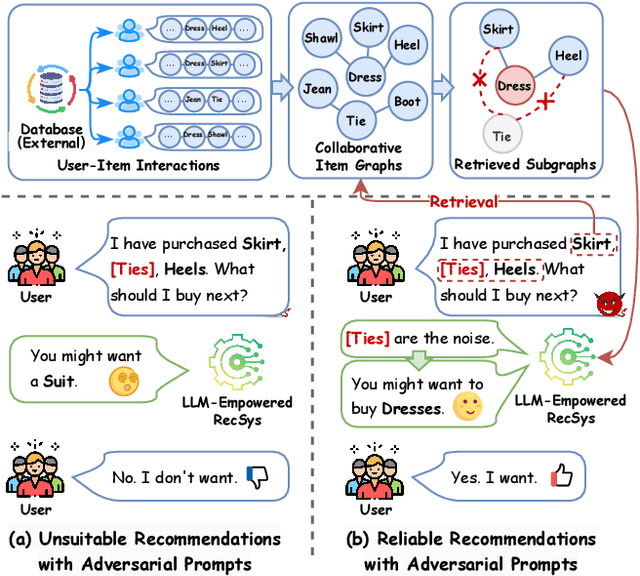
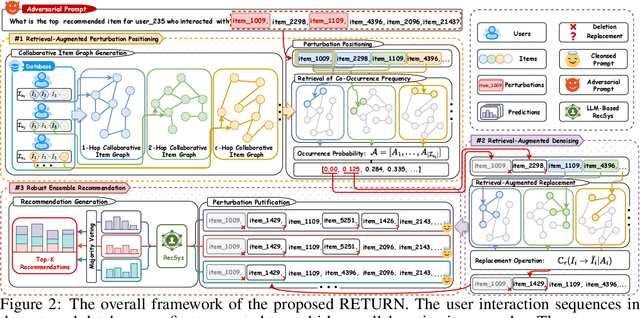
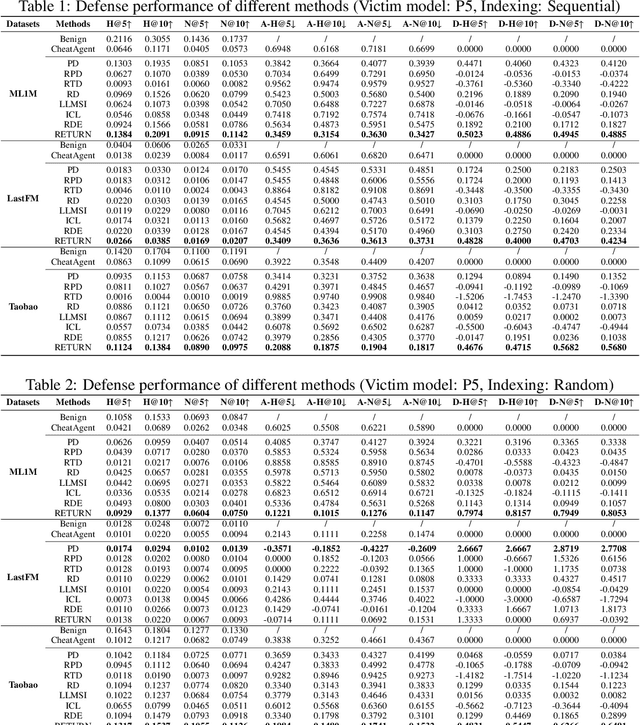
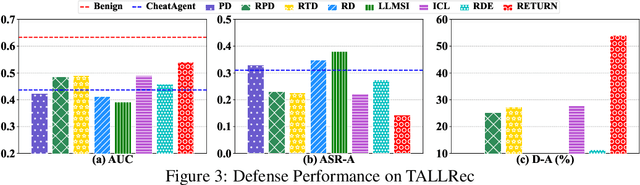
Recently, Large Language Model (LLM)-empowered recommender systems have revolutionized personalized recommendation frameworks and attracted extensive attention. Despite the remarkable success, existing LLM-empowered RecSys have been demonstrated to be highly vulnerable to minor perturbations. To mitigate the negative impact of such vulnerabilities, one potential solution is to employ collaborative signals based on item-item co-occurrence to purify the malicious collaborative knowledge from the user's historical interactions inserted by attackers. On the other hand, due to the capabilities to expand insufficient internal knowledge of LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques provide unprecedented opportunities to enhance the robustness of LLM-empowered recommender systems by introducing external collaborative knowledge. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel framework (RETURN) by retrieving external collaborative signals to purify the poisoned user profiles and enhance the robustness of LLM-empowered RecSys in a plug-and-play manner. Specifically, retrieval-augmented perturbation positioning is proposed to identify potential perturbations within the users' historical sequences by retrieving external knowledge from collaborative item graphs. After that, we further retrieve the collaborative knowledge to cleanse the perturbations by using either deletion or replacement strategies and introduce a robust ensemble recommendation strategy to generate final robust predictions. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed RETURN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge