Rethink Global Reward Game and Credit Assignment in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2019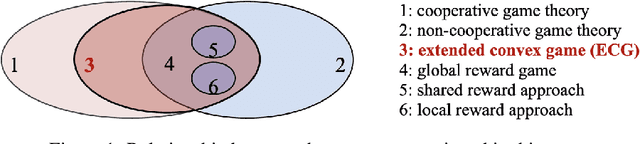


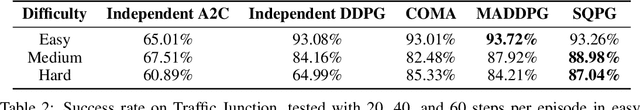
Cooperative game is a critical research area in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Global reward game is a subclass of cooperative games, where all agents aim to maximize cumulative global rewards. Credit assignment is an important problem studied in the global reward game. Most works stand by the view of non-cooperative-game theoretical framework with the shared reward approach, i.e., each agent is assigned a shared global reward directly. This, however, may give each agent an inaccurate feedback on his contribution to the group. In this paper, we introduce a cooperative-game theoretical framework and extend it to the finite-horizon case. We show that our proposed framework is a superset of the global reward game. Based on this framework, we propose an algorithm called Shapley Q-value policy gradient (SQPG) to learn a local reward approach that can distribute the cumulative global reward fairly, reflecting each agent's own contribution in contrast to the shared reward approach. We evaluate our method on the Cooperative Navigation, Prey-and-Predator and Traffic Junction, compared with MADDPG, COMA, Independent actor-critic and Independent DDPG. In the experiments, our algorithm shows better convergence than the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge