ResUNet-a: a deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2019


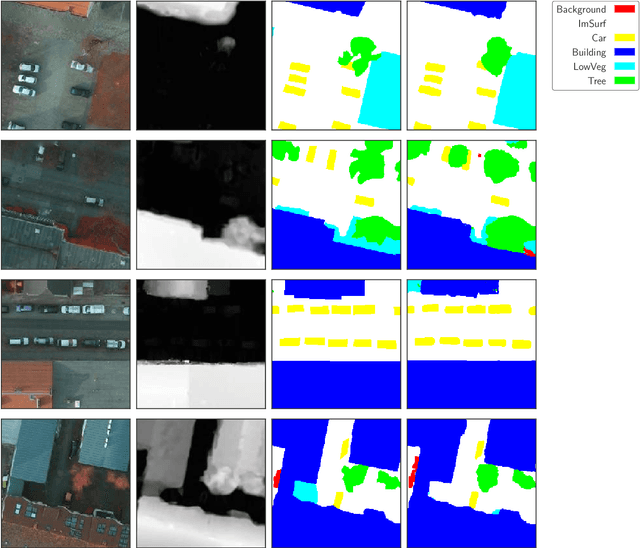
Scene understanding of high resolution aerial images is of great importance for the task of automated monitoring in various remote sensing applications. Due to the large within-class and small between-class variance in pixel values of objects of interest, this remains a challenging task. In recent years, deep convolutional neural networks have started being used in remote sensing applications and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance for pixel level classification of objects. Here we present a novel deep learning architecture, ResUNet-a, that combines ideas from various state-of-the-art modules used in computer vision for semantic segmentation tasks. We analyse the performance of several flavours of the Generalized Dice loss for semantic segmentation, and we introduce a novel variant loss function for semantic segmentation of objects that has better convergence properties and behaves well even under the presence of highly imbalanced classes. The performance of our modelling framework is evaluated on the ISPRS 2D Potsdam dataset. Results show state-of-the-art performance with an average F1 score of 92.1\% over all classes for our best model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge