Restricted Linearized Augmented Lagrangian Method for Euler's Elastica Model
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2019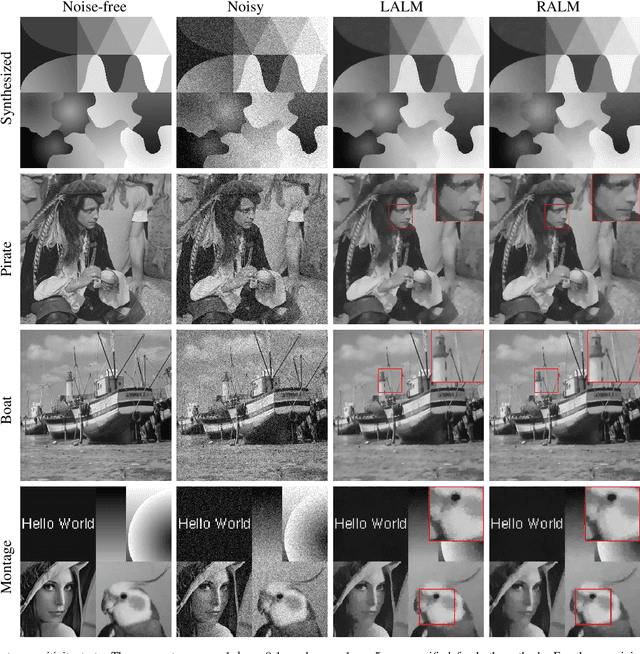
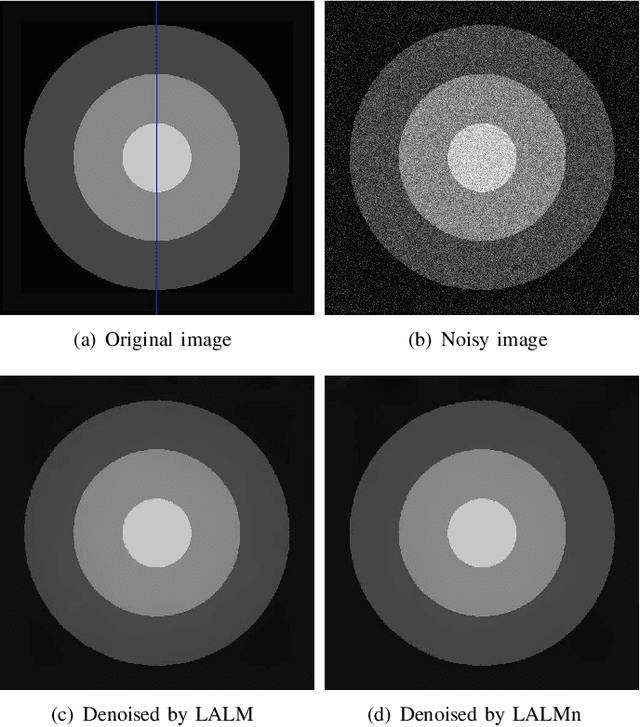
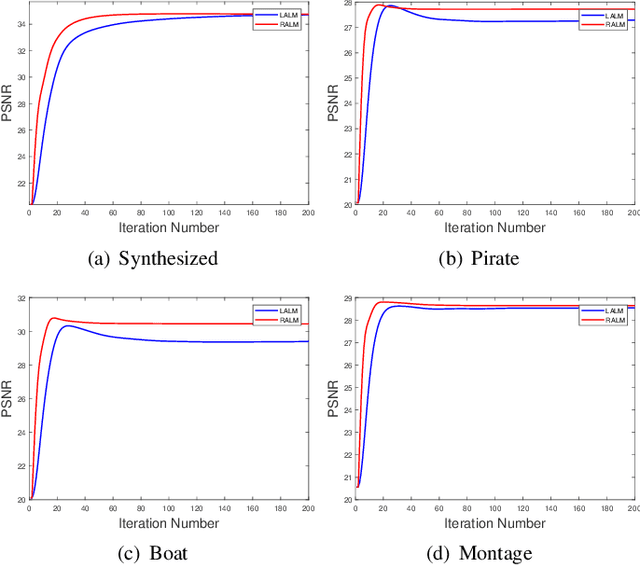

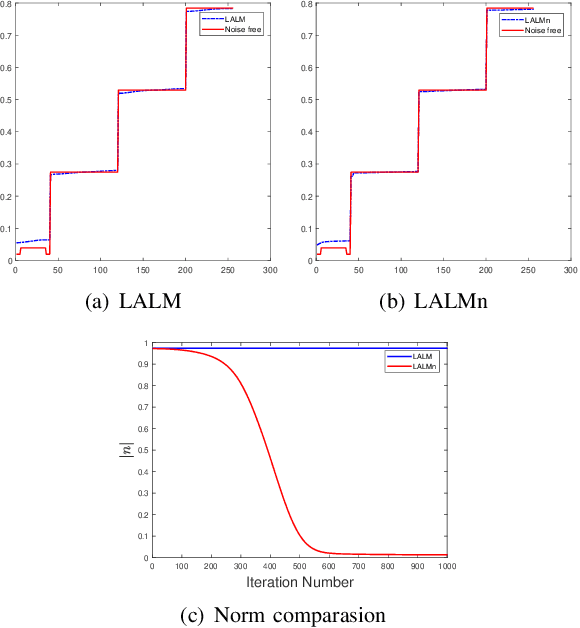
Euler's elastica model has been extensively studied and applied to image processing tasks. However, due to the high nonlinearity and nonconvexity of the involved curvature term, conventional algorithms suffer from slow convergence and high computational cost. Various fast algorithms have been proposed, among which, the augmented Lagrangian based ones are very popular in the community. However, parameter tuning might be very challenging for these methods. In this paper, a simple cutting-off strategy is introduced into the augmented Lagrangian based algorithms for minimizing the Euler's elastica energy, which leads to easy parameter tuning and fast convergence. The cutting-off strategy is based on an observation of inconsistency inside the augmented Lagrangian based algorithms. When the weighting parameter of the curvature term goes to zero, the energy functional boils down to the ROF model. So, a natural requirement is that its augmented Lagrangian based algorithms should also approach the augmented Lagrangian based algorithms formulated directly for solving the ROF model from the very beginning. Unfortunately, this is not the case for certain existing augmented Lagrangian based algorithms. The proposed cutting-off strategy helps to decouple the tricky dependence between the auxiliary splitting variables, so as to remove the observed inconsistency. Numerical experiments suggest that the proposed algorithm enjoys easier parameter-tuning, faster convergence and even higher quality of image restorations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge