Restricted Boltzmann Machine Flows and The Critical Temperature of Ising models
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2020
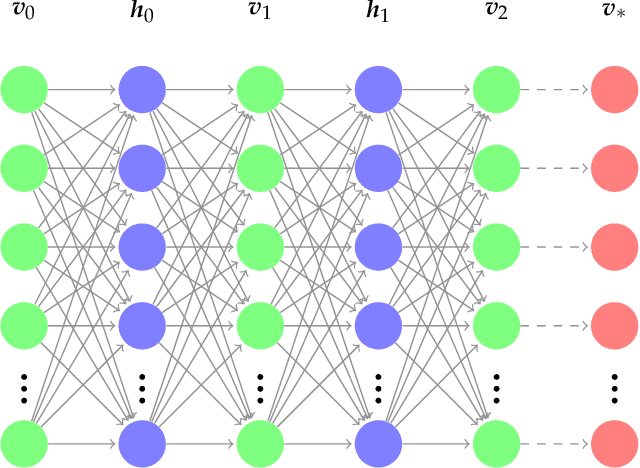


We explore alternative experimental setups for the iterative sampling (flow) from Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBM) mapped on the temperature space of square lattice Ising models by a neural network thermometer. This framework has been introduced to explore connections between RBM-based deep neural networks and the Renormalization Group (RG). It has been found that, under certain conditions, the flow of an RBM trained with Ising spin configurations approaches in the temperature space a value around the critical one: $ k_B T_c / J \approx 2.269$. In this paper we consider datasets with no information about model topology to argue that a neural network thermometer is not an accurate way to detect whether the RBM has learned scale invariance or not.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge