RespVAD: Voice Activity Detection via Video-Extracted Respiration Patterns
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2020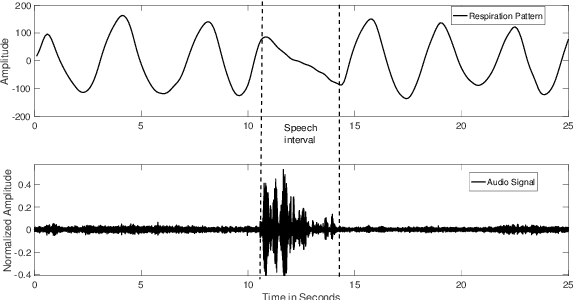

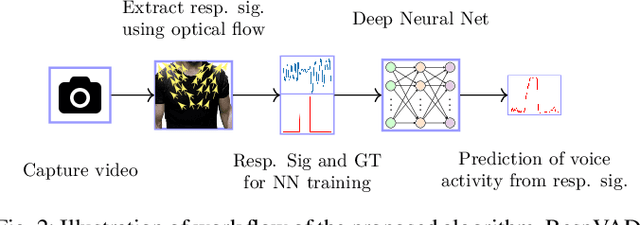

Voice Activity Detection (VAD) refers to the task of identification of regions of human speech in digital signals such as audio and video. While VAD is a necessary first step in many speech processing systems, it poses challenges when there are high levels of ambient noise during the audio recording. To improve the performance of VAD in such conditions, several methods utilizing the visual information extracted from the region surrounding the mouth/lip region of the speakers' video recording have been proposed. Even though these provide advantages over audio-only methods, they depend on faithful extraction of lip/mouth regions. Motivated by these, a new paradigm for VAD based on the fact that respiration forms the primary source of energy for speech production is proposed. Specifically, an audio-independent VAD technique using the respiration pattern extracted from the speakers' video is developed. The Respiration Pattern is first extracted from the video focusing on the abdominal-thoracic region of a speaker using an optical flow based method. Subsequently, voice activity is detected from the respiration pattern signal using neural sequence-to-sequence prediction models. The efficacy of the proposed method is demonstrated through experiments on a challenging dataset recorded in real acoustic environments and compared with four previous methods based on audio and visual cues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge