ReSCo-CC: Unsupervised Identification of Key Disinformation Sentences
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2020

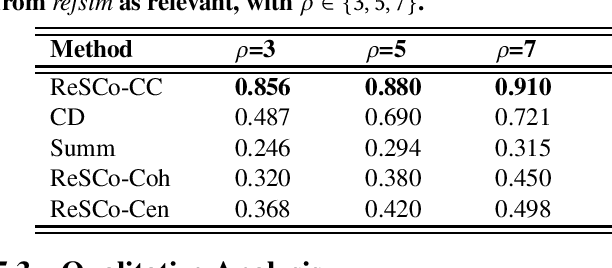

Disinformation is often presented in long textual articles, especially when it relates to domains such as health, often seen in relation to COVID-19. These articles are typically observed to have a number of trustworthy sentences among which core disinformation sentences are scattered. In this paper, we propose a novel unsupervised task of identifying sentences containing key disinformation within a document that is known to be untrustworthy. We design a three-phase statistical NLP solution for the task which starts with embedding sentences within a bespoke feature space designed for the task. Sentences represented using those features are then clustered, following which the key sentences are identified through proximity scoring. We also curate a new dataset with sentence level disinformation scorings to aid evaluation for this task; the dataset is being made publicly available to facilitate further research. Based on a comprehensive empirical evaluation against techniques from related tasks such as claim detection and summarization, as well as against simplified variants of our proposed approach, we illustrate that our method is able to identify core disinformation effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge