ResBench: Benchmarking LLM-Generated FPGA Designs with Resource Awareness
Paper and Code
Mar 11, 2025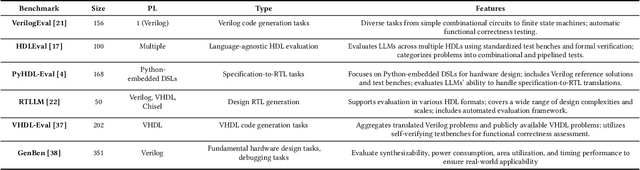

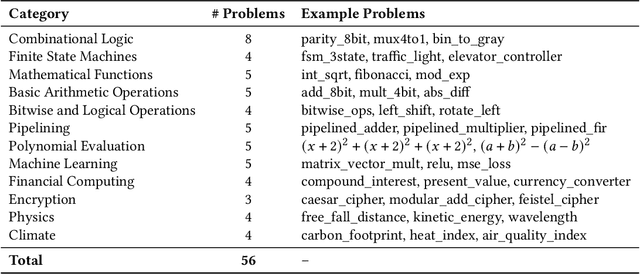
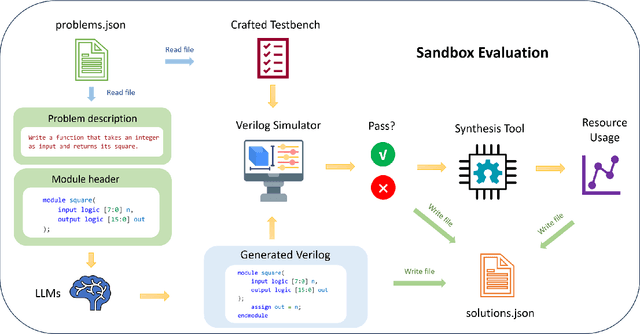
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are widely used in modern hardware design, yet writing Hardware Description Language (HDL) code for FPGA implementation remains labor-intensive and complex. Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a promising tool for automating HDL generation, but existing benchmarks for LLM HDL code generation primarily evaluate functional correctness while overlooking the critical aspect of hardware resource efficiency. Moreover, current benchmarks lack diversity, failing to capture the broad range of real-world FPGA applications. To address these gaps, we introduce ResBench, the first resource-oriented benchmark explicitly designed to differentiate between resource-optimized and inefficient LLM-generated HDL. ResBench consists of 56 problems across 12 categories, covering applications from finite state machines to financial computing. Our evaluation framework systematically integrates FPGA resource constraints, with a primary focus on Lookup Table (LUT) usage, enabling a realistic assessment of hardware efficiency. Experimental results reveal substantial differences in resource utilization across LLMs, demonstrating ResBench's effectiveness in distinguishing models based on their ability to generate resource-optimized FPGA designs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge