Representation Improvement in Latent Space for Search-Based Testing of Autonomous Robotic Systems
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2025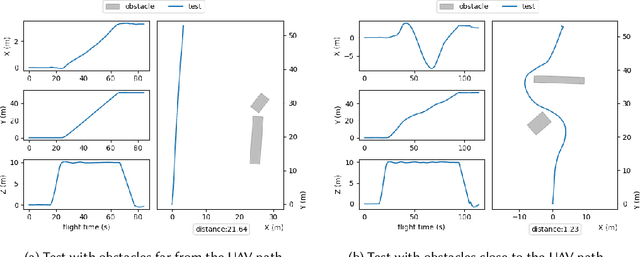
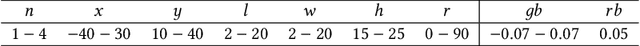
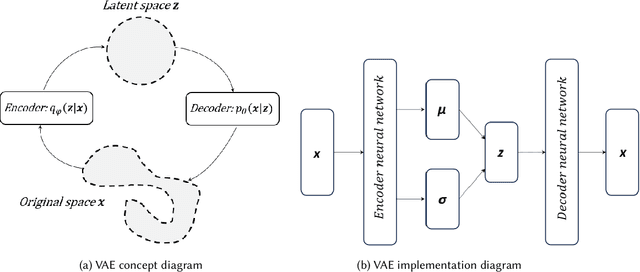
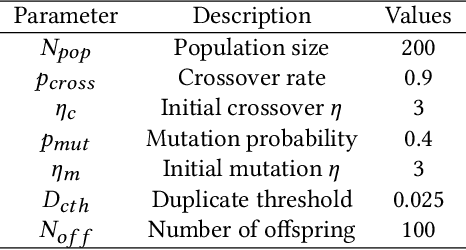
Testing autonomous robotic systems, such as self-driving cars and unmanned aerial vehicles, is challenging due to their interaction with highly unpredictable environments. A common practice is to first conduct simulation-based testing, which, despite reducing real-world risks, remains time-consuming and resource-intensive due to the vast space of possible test scenarios. A number of search-based approaches were proposed to generate test scenarios more efficiently. A key aspect of any search-based test generation approach is the choice of representation used during the search process. However, existing methods for improving test scenario representation remain limited. We propose RILaST (Representation Improvement in Latent Space for Search-Based Testing) approach, which enhances test representation by mapping it to the latent space of a variational autoencoder. We evaluate RILaST on two use cases, including autonomous drone and autonomous lane-keeping assist system. The obtained results show that RILaST allows finding between 3 to 4.6 times more failures than baseline approaches, achieving a high level of test diversity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge