Reliability of deep learning models for anatomical landmark detection: The role of inter-rater variability
Paper and Code
Nov 26, 2024
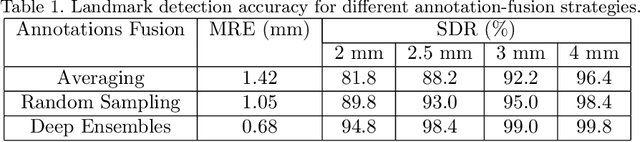
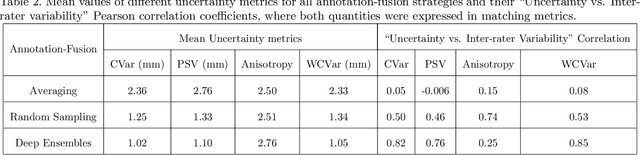
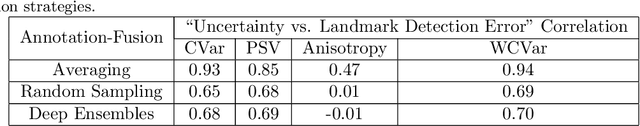
Automated detection of anatomical landmarks plays a crucial role in many diagnostic and surgical applications. Progresses in deep learning (DL) methods have resulted in significant performance enhancement in tasks related to anatomical landmark detection. While current research focuses on accurately localizing these landmarks in medical scans, the importance of inter-rater annotation variability in building DL models is often overlooked. Understanding how inter-rater variability impacts the performance and reliability of the resulting DL algorithms, which are crucial for clinical deployment, can inform the improvement of training data construction and boost DL models' outcomes. In this paper, we conducted a thorough study of different annotation-fusion strategies to preserve inter-rater variability in DL models for anatomical landmark detection, aiming to boost the performance and reliability of the resulting algorithms. Additionally, we explored the characteristics and reliability of four metrics, including a novel Weighted Coordinate Variance metric to quantify landmark detection uncertainty/inter-rater variability. Our research highlights the crucial connection between inter-rater variability, DL-models performances, and uncertainty, revealing how different approaches for multi-rater landmark annotation fusion can influence these factors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge