Relational Representation Distillation
Paper and Code
Jul 19, 2024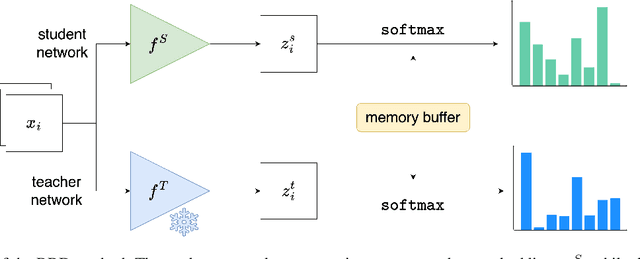
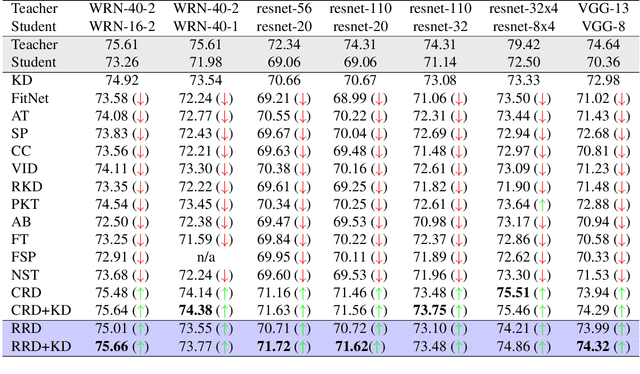
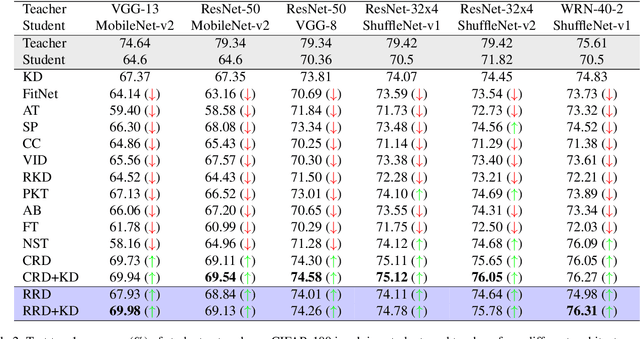
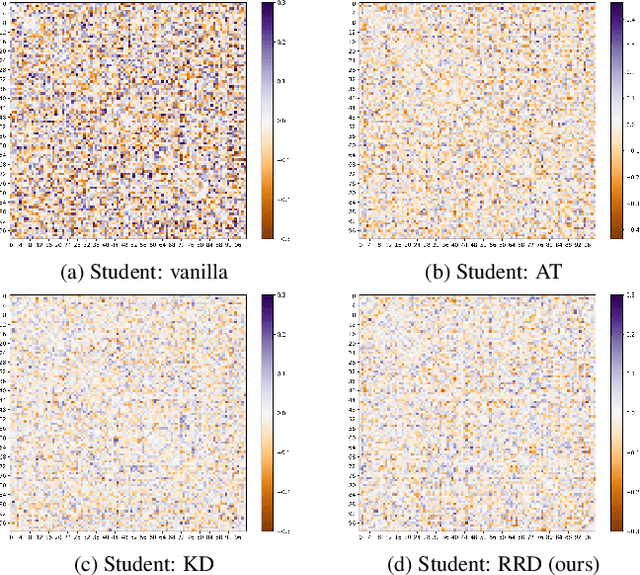
Knowledge distillation (KD) is an effective method for transferring knowledge from a large, well-trained teacher model to a smaller, more efficient student model. Despite its success, one of the main challenges in KD is ensuring the efficient transfer of complex knowledge while maintaining the student's computational efficiency. Unlike previous works that applied contrastive objectives promoting explicit negative instances, we introduce Relational Representation Distillation (RRD). Our approach leverages pairwise similarities to explore and reinforce the relationships between the teacher and student models. Inspired by self-supervised learning principles, it uses a relaxed contrastive loss that focuses on similarity rather than exact replication. This method aligns the output distributions of teacher samples in a large memory buffer, improving the robustness and performance of the student model without the need for strict negative instance differentiation. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on CIFAR-100, outperforming traditional KD techniques and surpassing 13 state-of-the-art methods. It also transfers successfully to other datasets like Tiny ImageNet and STL-10. The code will be made public soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge