Reinforcement learning using Deep Q Networks and Q learning accurately localizes brain tumors on MRI with very small training sets
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2020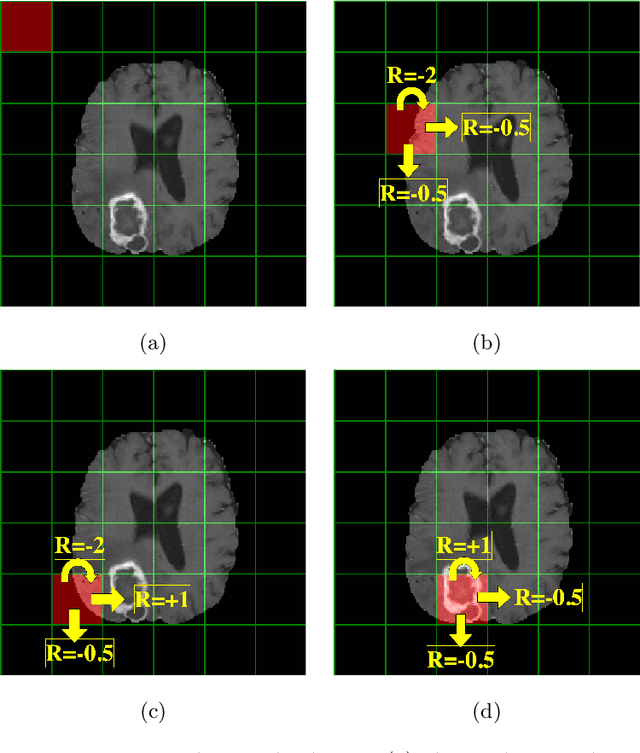
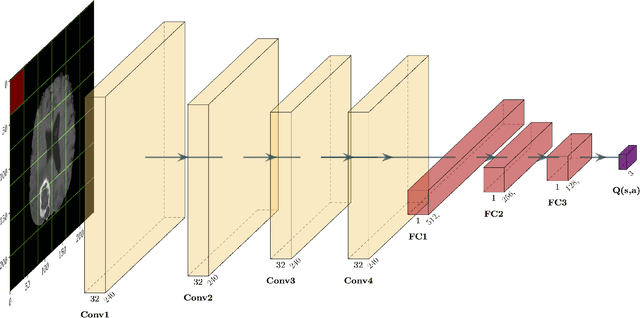
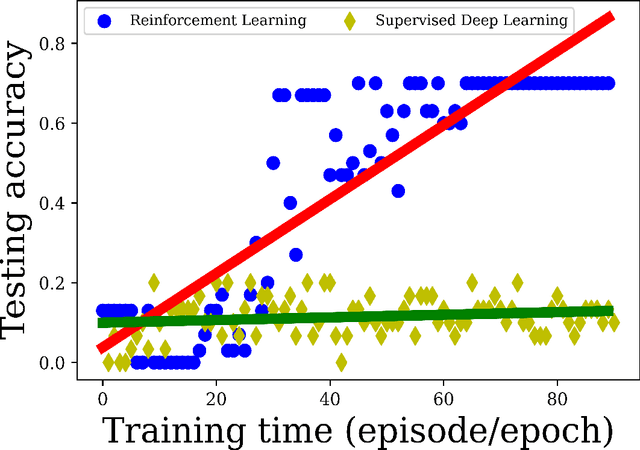
Purpose Supervised deep learning in radiology suffers from notorious inherent limitations: 1) It requires large, hand-annotated data sets, 2) It is non-generalizable, and 3) It lacks explainability and intuition. We have recently proposed Reinforcement Learning to address all threes. However, we applied it to images with radiologist eye tracking points, which limits the state-action space. Here we generalize the Deep-Q Learning to a gridworld-based environment, so that only the images and image masks are required. Materials and Methods We trained a Deep Q network on 30 two-dimensional image slices from the BraTS brain tumor database. Each image contained one lesion. We then tested the trained Deep Q network on a separate set of 30 testing set images. For comparison, we also trained and tested a keypoint detection supervised deep learning network for the same set of training / testing images. Results Whereas the supervised approach quickly overfit the training data, and predicably performed poorly on the testing set (11\% accuracy), the Deep-Q learning approach showed progressive improved generalizability to the testing set over training time, reaching 70\% accuracy. Conclusion We have shown a proof-of-principle application of reinforcement learning to radiological images, here using 2D contrast-enhanced MRI brain images with the goal of localizing brain tumors. This represents a generalization of recent work to a gridworld setting, naturally suitable for analyzing medical images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge