Reinforcement Learning in Healthcare: A Survey
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2019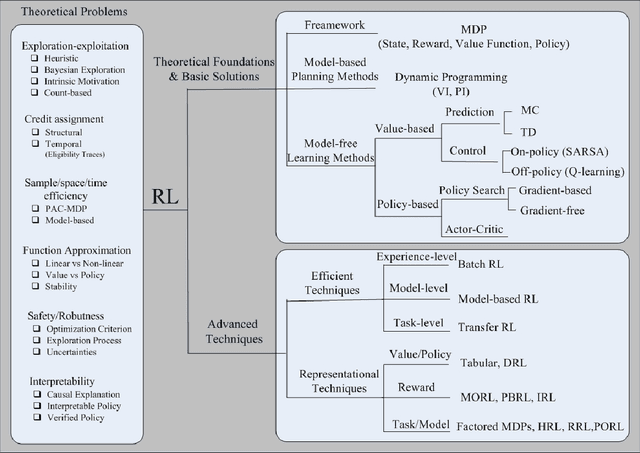
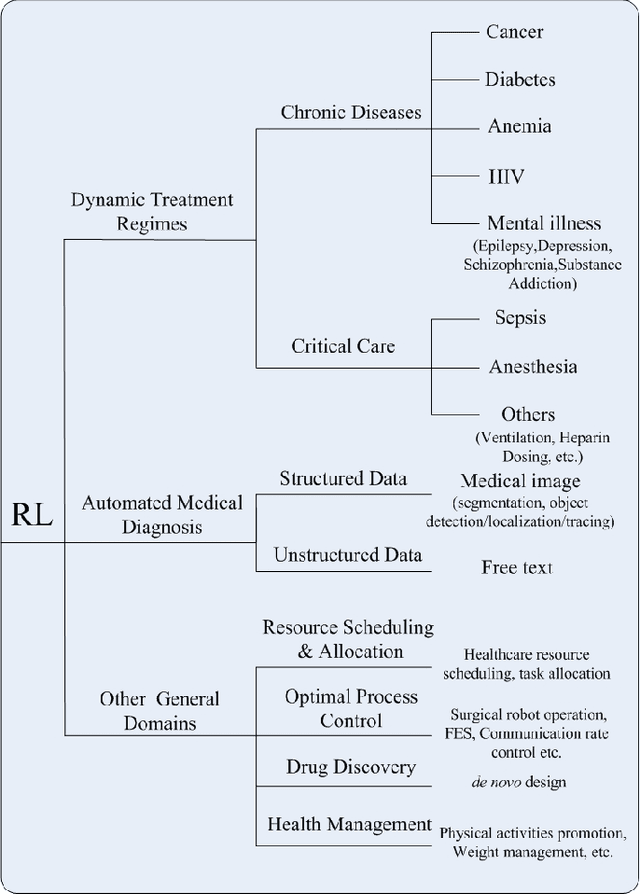
As a subfield of machine learning, \emph{reinforcement learning} (RL) aims at empowering one's capabilities in behavioural decision making by using interaction experience with the world and an evaluative feedback. Unlike traditional supervised learning methods that usually rely on one-shot, exhaustive and supervised reward signals, RL tackles with sequential decision making problems with sampled, evaluative and delayed feedback simultaneously. Such distinctive features make RL technique a suitable candidate for developing powerful solutions in a variety of healthcare domains, where diagnosing decisions or treatment regimes are usually characterized by a prolonged and sequential procedure. This survey will discuss the broad applications of RL techniques in healthcare domains, in order to provide the research community with systematic understanding of theoretical foundations, enabling methods and techniques, existing challenges, and new insights of this emerging paradigm. By first briefly examining theoretical foundations and key techniques in RL research from efficient and representational directions, we then provide an overview of RL applications in a variety of healthcare domains, ranging from dynamic treatment regimes in chronic diseases and critical care, automated medical diagnosis from both unstructured and structured clinical data, as well as many other control or scheduling domains that have infiltrated many aspects of a healthcare system. Finally, we summarize the challenges and open issues in current research, and point out some potential solutions and directions for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge