Reevaluating Loss Functions: Enhancing Robustness to Label Noise in Deep Learning Models
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2023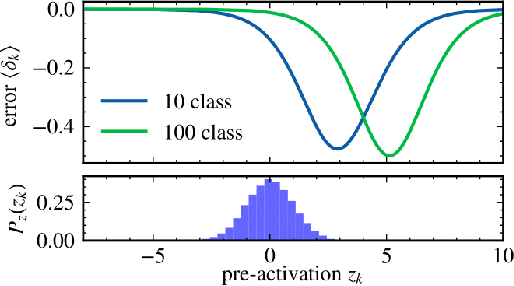
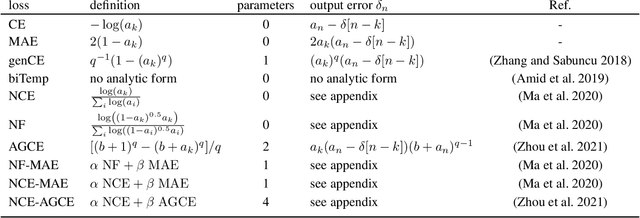
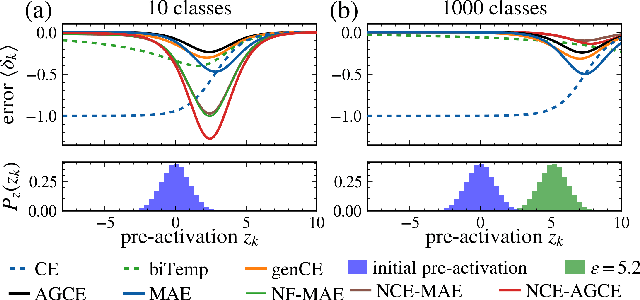
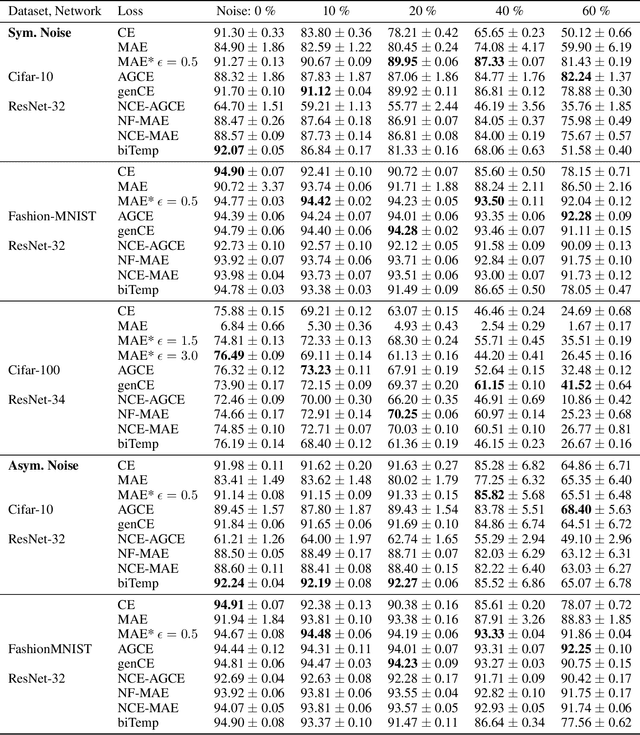
Large annotated datasets inevitably contain incorrect labels, which poses a major challenge for the training of deep neural networks as they easily fit the labels. Only when training with a robust model that is not easily distracted by the noise, a good generalization performance can be achieved. A simple yet effective way to create a noise robust model is to use a noise robust loss function. However, the number of proposed loss functions is large, they often come with hyperparameters, and may learn slower than the widely used but noise sensitive Cross Entropy loss. By heuristic considerations and extensive numerical experiments, we study in which situations the proposed loss functions are applicable and give suggestions on how to choose an appropriate loss. Additionally, we propose a novel technique to enhance learning with bounded loss functions: the inclusion of an output bias, i.e. a slight increase in the neuron pre-activation corresponding to the correct label. Surprisingly, we find that this not only significantly improves the learning of bounded losses, but also leads to the Mean Absolute Error loss outperforming the Cross Entropy loss on the Cifar-100 dataset - even in the absence of additional label noise. This suggests that training with a bounded loss function can be advantageous even in the presence of minimal label noise. To further strengthen our analysis of the learning behavior of different loss functions, we additionally design and test a novel loss function denoted as Bounded Cross Entropy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge