Reducing Overestimation Bias in Multi-Agent Domains Using Double Centralized Critics
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2019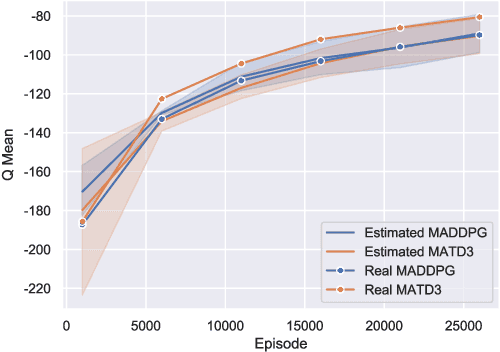
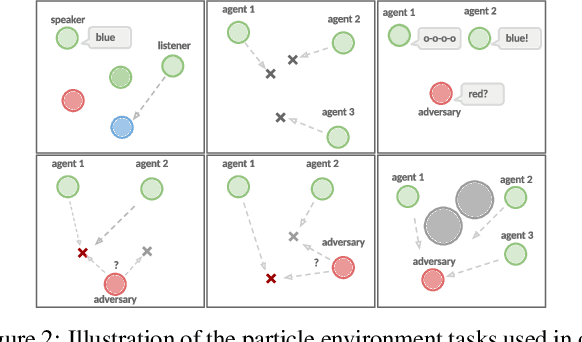
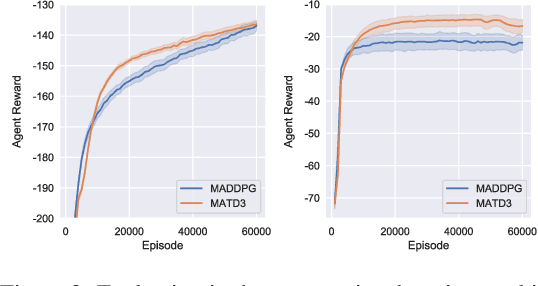
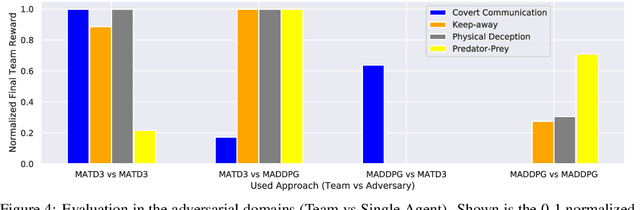
Many real world tasks require multiple agents to work together. Multi-agent reinforcement learning (RL) methods have been proposed in recent years to solve these tasks, but current methods often fail to efficiently learn policies. We thus investigate the presence of a common weakness in single-agent RL, namely value function overestimation bias, in the multi-agent setting. Based on our findings, we propose an approach that reduces this bias by using double centralized critics. We evaluate it on six mixed cooperative-competitive tasks, showing a significant advantage over current methods. Finally, we investigate the application of multi-agent methods to high-dimensional robotic tasks and show that our approach can be used to learn decentralized policies in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge