Reducing Communication in Graph Neural Network Training
Paper and Code
May 07, 2020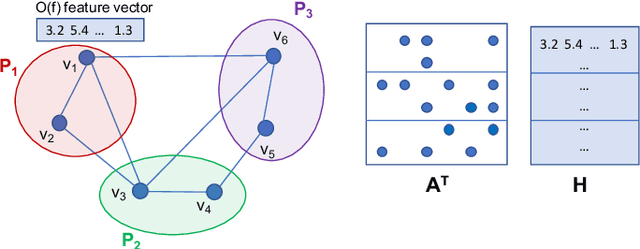


Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are powerful and flexible neural networks that use the naturally sparse connectivity information of the data. GNNs represent this connectivity as sparse matrices, which have lower arithmetic intensity and thus higher communication costs compared to dense matrices, making GNNs harder to scale to high concurrencies than convolutional or fully-connected neural networks. We present a family of parallel algorithms for training GNNs. These algorithms are based on their counterparts in dense and sparse linear algebra, but they had not been previously applied to GNN training. We show that they can asymptotically reduce communication compared to existing parallel GNN training methods. We implement a promising and practical version that is based on 2D sparse-dense matrix multiplication using torch.distributed. Our implementation parallelizes over GPU-equipped clusters. We train GNNs on up to a hundred GPUs on datasets that include a protein network with over a billion edges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge