Real Time Video Quality Representation Classification of Encrypted HTTP Adaptive Video Streaming - the Case of Safari
Paper and Code
Feb 19, 2016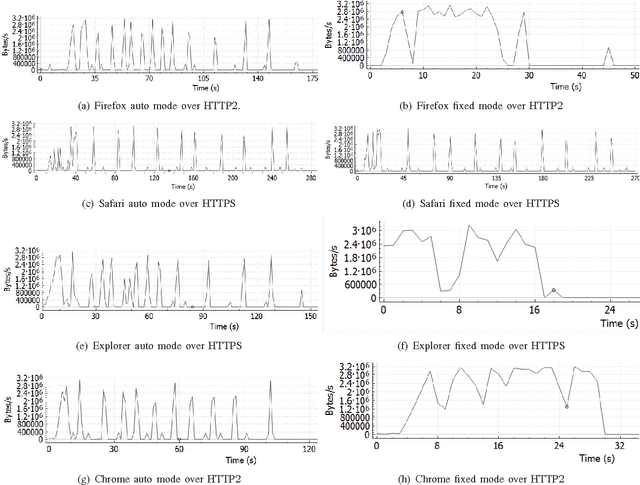
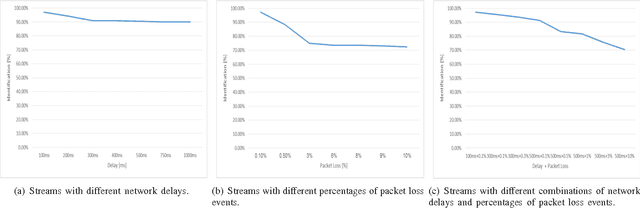
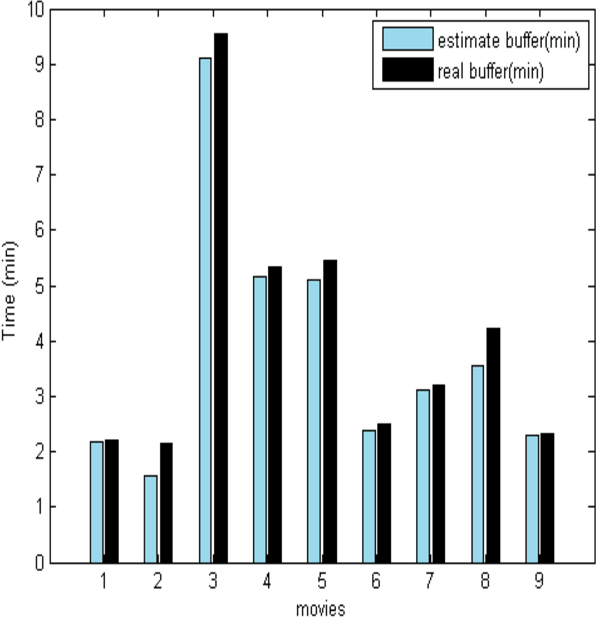

The increasing popularity of HTTP adaptive video streaming services has dramatically increased bandwidth requirements on operator networks, which attempt to shape their traffic through Deep Packet Inspection (DPI). However, Google and certain content providers have started to encrypt their video services. As a result, operators often encounter difficulties in shaping their encrypted video traffic via DPI. This highlights the need for new traffic classification methods for encrypted HTTP adaptive video streaming to enable smart traffic shaping. These new methods will have to effectively estimate the quality representation layer and playout buffer. We present a new method and show for the first time that video quality representation classification for (YouTube) encrypted HTTP adaptive streaming is possible. We analyze the performance of this classification method with Safari over HTTPS. Based on a large number of offline and online traffic classification experiments, we demonstrate that it can independently classify, in real time, every video segment into one of the quality representation layers with 97.18% average accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge