Real-Time Capable Micro-Doppler Signature Decomposition of Walking Human Limbs
Paper and Code
Nov 25, 2017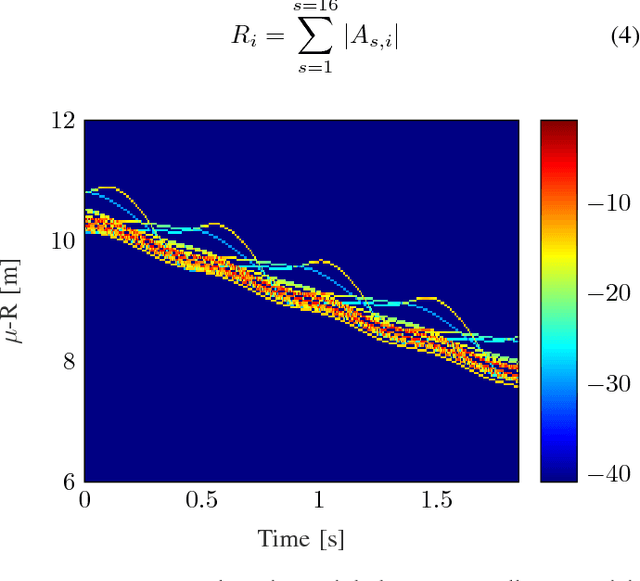
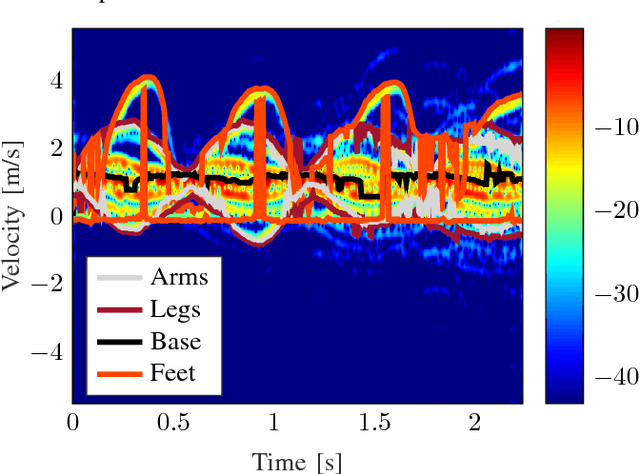
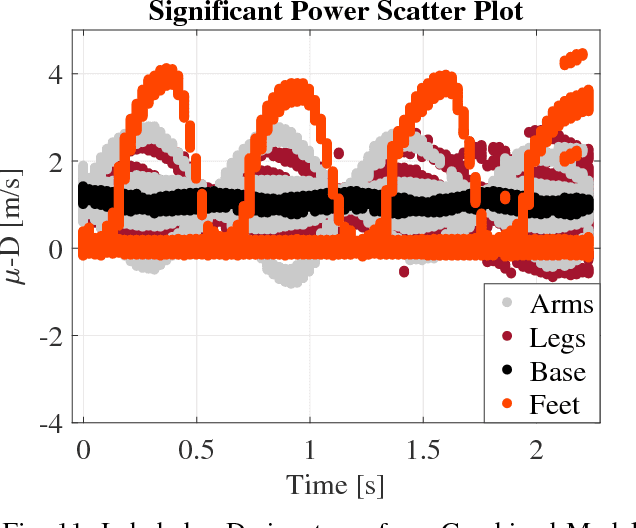
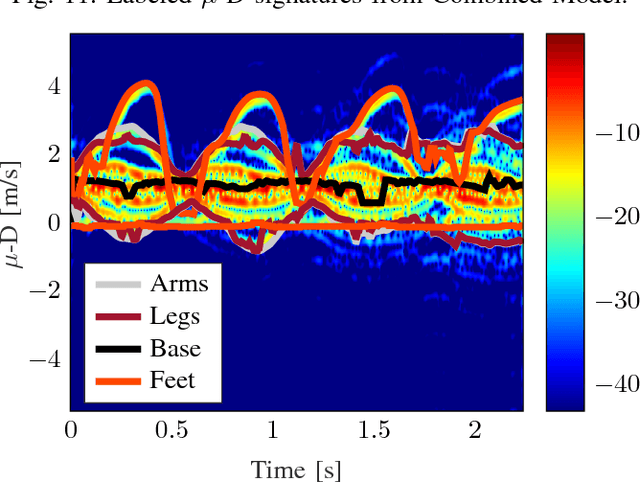
Unique micro-Doppler signature ($\boldsymbol{\mu}$-D) of a human body motion can be analyzed as the superposition of different body parts $\boldsymbol{\mu}$-D signatures. Extraction of human limbs $\boldsymbol{\mu}$-D signatures in real-time can be used to detect, classify and track human motion especially for safety application. In this paper, two methods are combined to simulate $\boldsymbol{\mu}$-D signatures of a walking human. Furthermore, a novel limbs $\mu$-D signature time independent decomposition feasibility study is presented based on features as $\mu$-D signatures and range profiles also known as micro-Range ($\mu$-R). Walking human body parts can be divided into four classes (base, arms, legs, feet) and a decision tree classifier is used. Validation is done and the classifier is able to decompose $\mu$-D signatures of limbs from a walking human signature on real-time basis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge